## I. INTRODUCTION
Widespread criminal violence across the world has informed critical stakeholders especially those in government to consider a paradigm shift in addressing increasing crime surges. Traditional policing techniques as noted by smith [1] have become a subject of public discourse, with many questioning their effectiveness. Despite increased funding and personnel, traditional policing techniques alone may not be sufficient to counter exponential rise in global crime. Police personnel and other security agencies are already overwhelmed and now struggling to keep pace with modern tactics employed by criminals [11]. The escalating dynamism of criminals exposes the significant shortfall in both manpower and innovative technology that are necessary to adequately combat these challenges [1].
The persistence loss of life, and properties from crimes such as arson, armed robbery and kidnapping, coupled with organized crimes, and mob actions have invited the urgent need for preemptive innovative approaches to crime detection and predictions across the globe. Traditional methods have shown its inadequacy due to the unpredictable nature of crimes which seems unforeseeable to the public. However emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence offer a promising solution, capable of detecting and predicting activities with sufficient training data [2].
Several approaches to crime predictions in recent times have been toward predictive modeling. With the increasing surveillance technologies such as CCTV, researchers are increasingly focusing on object detection algorithms. These methods enable CCTV systems as a vigilant observer, supplying in real-time data to computer vision models for immediate analysis. A common of these algorithms is the use ofYOLOv4 short for "You Only Look Once." Which is known for its efficiency and accuracy in object detection. This paper proposes the use Yo1ov4 to predict violent crime and persons who are more likely to commit crime and identify individuals who are likely to commit crimes in the future.
Yolov4 by default is an object detection algorithm this research however makes a unique contribution by integrating this algorithm (Yolov4) into predictive models, thereby enhancing the predictive capabilities of traditional surveillance systems (CCTV). This research unlike existing methods is leveraging on an advanced object detection algorithm to provide accurate and timely predictions of criminal activities.
The remainder of this paper is arranged as follows: section II reviews related theories and methodologies that have been used to detect and predict crimes. Section III discusses the materials and methods while the presentation of our findings, results, and discussion is contained in Section IV. The study's conclusion and recommendations are in Section V.
## II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Over the years, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have proven highly effective processing images and detecting objects. CNNs specialized in image recognition, consists of multiple layers that perform distinct but well-connected tasks. CNNs are neural networks specialized for image recognition, structured with multiple layers, each executing distinct tasks. The input layer receives the Images dataset which then processed by convolutional layer to extract essential features. The pooling layer reduces output dimensions by pooling pixels from fixed-size squares, enhancing error tolerance and the fully connected layer channels this output to multiple neurons corresponding to detected objects. Finally the output layers identifies the object class and its coordinates [3], [4].
CNNs exhibit versatility, capable of discerning diverse objects like humans, vehicles, animals, and even individual alphabets. All object detection algorithms one way or another somehow involve convolutional neural networks and thus make CNN an important architecture in the Yolov4 algorithms and single-shot detection models which are two of the modern detection models available.
### a) CNN-based Methods
Several researchers have applied CNN-based methods to crime prediction. For example [5]developed a system to detects firearms and knives captured by cameras, using principal component analysis (PCA) and MPEG-7 with a window technique to achieve an accuracy of $96.96\%$ similarly,[6], used faster R-CNN to detect firearms, achieving an accuracy of $93.1\%$. These methods demonstrate the capability of CNN in enhancing crime detection using an advanced image processing methods
### b) Facial Recognition
Facial expression is another critical area in Aldriven crime prediction techniques. According to [7] facial recognition has modernized criminal profiling and surveillance which therefore increase the efficiency of traditional policing. [1] were motivated by their belief that if it was possible to know and determine someone that is sad based on facial expression then it may also be possible to know criminals just by facial expression, this motivation led them to the results they arrived at in their paper titled "Advanced Convolutional Neural Network Paradigms-Comparison of VGG16 with Resnet50 in Crime detection". The author used A-CNN to extract distinctive features of criminals and non-criminals and was able to classify criminal and noncriminal faces, achieving remarkable training accuracy of $98.10\%$ and $95.05\%$ on VGG16 and Resnet50respectively. This demonstrates the potential of facial recognition in predicting criminals based on visual cues.
### c) Traditional Methods
Other methods for predicting crimes include stingray an outdated but still common method used by police to track criminals [20], polygraph, a lie detector invented in 1920s was a significant milestone in detecting criminal suspects by measuring their psychological responses. However, with the current dynamism of the criminal intellects, many suspects having studied the working principle of polygraphs which are sensory of human pulses now evade being detected by polygraph rendering these methods less effective over the time [21]
### d) Literature Review Gaps
While conventional CNN-based methods and facial recognition technologies show promise in various applications, they present challenges such as potential biases and limitations in predicting criminal activities in pre-crime scenarios. Additionally, traditional methods like polygraph tests and stingray technology are becoming less effective as criminals find ways to evade detection.
The evolving sophistication of criminal behaviour underscores the critical need for more integrated approaches to crime prediction. This study aims to address this need by utilizing YOLOv4 to enhance crime prediction models. YOLOv4 offers advantages in real-time processing capabilities, speed, and accuracy, making it particularly suitable for applications that require live monitoring, such as surveillance of crime hotspots. This will be further enhanced through the implementation of Python scripts to assess the culpability of individuals in pre-crime scenarios upon detection of any criminal weapons on a subject.
## III. MATERIALS AND METHODS
This section explores the methodologies used to achieve the results contained in section V. The methods here entirely depend on Yolov4, which uses darknet53 as a framework. However, because of the peculiarity of this study, our model was trained almost from scratch on a custom dataset. Also included in this section are hardware configuration, processes, and techniques involved in building custom object detectors specifically for the prediction of crimes.
### a) Novelty
The crux of this research lies in its innovative approach to detecting sub-objects, specifically weapons, on individuals, thereby enabling the identification of potentially high-risk individuals within precrime scenarios. This technological advancement holds the promise of revolutionizing the landscape of law enforcement and security protocols, ushering in a new era of initiative-taking crime mitigation strategies.
By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and cutting-edge algorithms, this research not only seeks to enhance the efficacy of law enforcement agencies but also aims to safeguard communities by pre-empting criminal incidents before they transpire. The fusion of technology and criminology encapsulated in this study heralds a future where predictive analytics and pre-emptive interventions are poised to redefine the dynamics of crime prevention.
### b) Data Collection and Processing
## i. Data Acquisition
Implementing a Yolov4-based crime prediction for this research paper requires quite an enormous dataset. The dataset for training was carefully sourced, exclusively with the intended result in mind. For the system development, we essentially utilized secondary dataset. video dataset from crime video clips were acquired from royalty free sites.
These instances were created to mimic criminals and criminal intents upon which our system would be finally tested to know if the model generalizes well to identifying a person holding a firearm, wandering suspiciously, persons with formidable looks, including face-masking ruffians, and thus classify them as High-
Risk based on predefined policies set as antisocial and criminal attributes in the society.
Additionally, we augmented our dataset by sourcing images with additional videos of weapons online using Google Chrome "Download all" extension and incorporated the UCF-crime dataset, which includes real-life videos and frames from surveillance cameras with labels such as assault and robbery [22]. Here is the list of weapons trained.
- Gun (Shotgun, Handgun, Riffle)
- Knives
 Fig. 1: UCF-Dataset [22]
## ii. Data Annotation
Data annotation is the categorization and labeling of data for artificial intelligence applications. For this study we manually labelled all frames using Yolo annotation tools particularly labelimg. Which therefore ensure accurate representation of objects.
The two Annotation tools for YOLO are:
1. Labeling (The labeling used to label still images)
2. Dark label (Dark label used to annotate video footage)
Labelimg can be installed using "pip install labelimg" for Linux and window users and can be launched by "labellmg"
We used labelimg because of the following reasons.
- Labellmg is easy to install.
- Convert directly to Yolov4 format.
- Open source.
The labelling tool was used to label the five classes of interest which are the following.
- Person
- Handgun
- Shotgun
- Knife
- Riffle
Annotating a dataset is the art of labeling objects and storing the coordinates of the objects [19]. In this design, and as earlier stated, labeling involves placing a rectangular box on the object and this automatically gets the coordinates of the object and is stored in text files. The text files (.txt) contain the following.
- Class Name
- Object Center Coordinates $(x, y)$
- Object Dimensions (width, height)
This together form the is termed the Yolo annotation format
## iii. Annotation format
During the annotation of the dataset, five things happen simultaneously, and they are.
a. Class Name
b. Object center coordinates in $x =$ Center $X/ImageWidth$
c. Object center coordinates in y = Center y/ImageHeight
d. Object width = ObjectWidth/ImageWidth
e. Object Height = ObjectHeight/ImageHeight
### c) System Algorithm Framework
YOLO, from the name that implies "You-Only-Look-Once" is an algorithm that takes an entire image at once and predicts for these boxes the bounding box coordinates and class probabilities [8].YOLO's most significant advantage is its unprecedented pace, it is speedy, and it can run 45 frames per second. Among the earliest versions of YOLO, version 4 is the fastest and most accurate in detecting objects.
The proposed algorithm, YOLO version 4, consists of 53 convolution layers. The architecture is made up of three different layer forms. Firstly, the residual layer is formed when the activation is easily forwarded to an inner-layer neural network [9]. In a residual setup, the result of layer one is summed to the output of layer 2. The second is the detection layer which performs detection at three different scales or stages. The size of the grids is increased for detection. The third is the up-sampling layer which increases the spatial resolution. Here the image is up-sampled before it is scaled. Also, the concatenation operation is used to concatenate the outputs of the previous layer to the presentation layer. The addition operation is used to add previous layers.
Figure 2.0 shows the architecture of yolov4. For clarity's sake and especially for our use case, the system architecture takes in our captured videos as input images; these caught videos are our dataset which was passed through the yolov4 object detection algorithm. In the yolov4 object detection module, the Yolo takes input frames first, and these frames are divided into grids, say $3 \times 3$, and on each grid, there is image classification and localization.
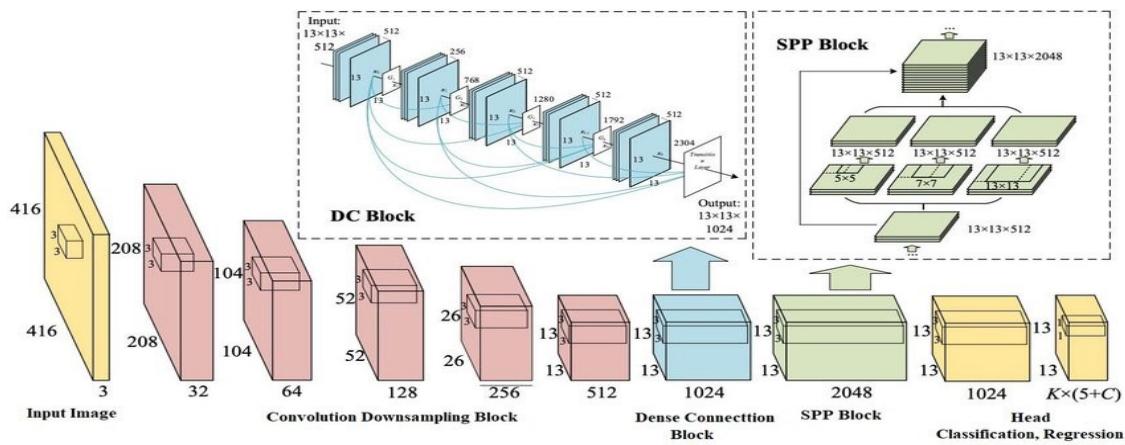 Fig. 2: YOLOv4 computer vision architecture [10]
### d) Model Setup
We used yolov4 with Darknet53 as the backbone. The configuration file (.cfg) was modified to suit our custom dataset with its five classes
- Setting up the.cfg file
To Train a custom dataset on the darknet framework requires cloning of AlexAB repository into the local directory using "git clone" and then reconfiguring thecfg file that is contained inside the darknetcfg folder of the cloned repository.
The.cfg file is replicated and the following design parameters are modified.
1. Image Dimensions: Set to 320x320 to fit memory constraints
2. Batch Size: 64, split into mini-batches for processing
3. Max Batches: 10,000, calculated as C×2000where C is the number of classes
4. Steps: $80\%$ and $90\%$ of max batches
5. Filters: Set to 30, calculated as $(\mathbb{C} + 5)\times 3$
6. Learning Rate: Set at 0.001
After all these changes in thecfg file, it was then saved and named "yolo-object.cfg" we then split the dataset into training and test set at 80/20 ratios.
- Setting Up Meta Data (obj)
The following metadata was additionally created;
i. Obj-names: It contained the names of the classes.
ii. obj.data contains
1. Total number of our classes $= 5$
2. The training and validation path,
3. Path to our obj. names
4. The directory where our weights would be saved.
### e) Evaluation Metrics Performance Metrics
We used the following metrics to evaluate the performance of our model.
- Mean average precision (mAP): It was the standard performance metric for an object detection model. It is the common way of seeing how novel the algorithm performs over the individual classes and the whole model [16]. It combines two important aspects: precision and recall, detailing a comprehensive model's ability to locate and classify objects in each frame. To compute mAP, precision-recall curves are constructed for each class of objects in our dataset. These curves plot precision against recall at different confidence score thresholds. The area under the curves was then averaged across all object classes [17]. The mAP is a valuable metric for knowing the accuracy of object detection models. It offers a balanced evaluation by
considering precision and recall, making it particularly suitable for object detection and classification problems.
$$
\mathrm {m} A P = \frac {1}{N} \sum_ {i = 1} ^ {N} A P _ {i} \tag {5}
$$
Where,
$$
N = Number of classes
$$
$\mathsf{AP}_{i} =$ Average precision for each class i.
- Precision: Precision tells the proportion of correctly identified objects out of all the detections made by the model [18].
$$
\text{Precision} = \frac{T P}{T P + F P} \tag{6}
$$
Where.
$$
TP= True Positive,
$$
$$
FP = False Positive
$$
- Recall: It measures the model's ability to find all relevant objects, minimizing false negatives [18].
$$
\text{Recall} = \frac{T P}{T P + F N} \tag{7}
$$
Here
$$
FN= False Negative.
$$
- F1 Value
The F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall and provides a balance between the two metrics.
It is calculated as:
$$
[F1 Score = 2 \times times \frac{Precision \times times Recall}{Precision + Recall}]
$$
(12) For simplicity,
- Precision focuses on the accuracy of positive predictions.
- Recall focuses on the proportion of actual positives that were correctly identified.
- F1 score provides a balance between precision and recall, especially when there is an uneven class distribution.
### f) Justification
Yolov4 which by default uses darknet53 was selected for its speed and accuracy in real-time. It's capable of processing 45 frames per second. Custom training was necessary due to the specificity of our crime scenarios and the need for tailored objection detection.
### g) Deep SORT Algorithm
Deep-SORT, an advanced tracking algorithm, enhances the Hungarian algorithm by integrating appearance information to link new detections to previously identified objects. Stemming from SORT, Deep-SORT employs deep learning techniques, using detection models likeYOLO or Faster R-CNN to locate human figures in video frames [12]. It assigns unique embeddings to objects, crucial for tracking across frames [13]. Deep-SORT excels in associating detections across frames, facilitated by the Hungarian algorithm and Kalman filtering, which mitigates inaccuracies and handles occlusions seamlessly. The algorithm optimizes assignment using a cost function that balances spatial and visual distances between detections and tracks [14].
The spatial distance, represented by mahala Nobis distance, which is calculated as in equation 7, accounts for predicted positions, while visual distance measures appearance dissimilarity using feature vectors from a residual neural network. Cosine distance serves as the similarity metric. Appearance descriptors are normalized, enabling cosine distance calculations. The process ensures robust tracking in crowded and challenging environments [15].
$$
\text{spatial}(i,j) = \left(x_{j} - x^{\wedge}_{i}\right) \cdot S_{i-1} \cdot \left(x_{j} - x^{\wedge}_{i}\right) \tag{7}
$$
Where.
$xj$ is the centroid (or other representative point) of the detected bounding box $j$.
$x^{\wedge}i$ is the predicted centroid of the tracked object $I$ based on its last known position.
$S_{i}$ is the covariance matrix associated with the predicted position of the tracked object $i$.
$T$ denotes the transpose operation.
## IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The research was conducted on core i5 HP Pavilion with 16GB RAM, a 4 GB Nvidia dedicated graphics card (GPU 1050ti), CUDA 10.1, and Cudnn7.6 on an Ubuntu system distribution. We implemented this research using the YOLOv4 darknet framework cloned from the AlexAB repository. The dataset was a mix of data from a UCF dataset of known criminals, and open-source data of images of guns, knives, and persons. Training this model requires careful annotation of images using a frame-by-frame annotation technique. The Center coordinates in X, Y, the object widths and heights, and the classes they belong to were determined simultaneously during the process of annotation using labelimg. This positioning of images was crucial during training to ensure accurate object localization and class recognition. The training was conducted on 3317 datasets, specially selected for this research, in 64 batches over 10000 iterations. The performance of our model is shown in Fig 3 (a) and Fig 3 (b) below.
{"code_caption":[],"code_content":[{"type":"text","content":"[yolo] params: iou loss: ciou (4), iou norm: 0.07, obj_norm: 1.00, \ncla_norm: 1.00, delta_norm: 1.00, scale_x_y: 1.05 \nnms-kind: greedynorms (1), beta = 0.600000 \nTotal BFLOPS 59.592 \navg Outputs = 490304 \nAllocate additional workspace_size = 52.44 MB \nLoading weights from /mydrive/Model/training/yolo-object_lastweights... \nseen 64, trained: 640 K-images (10 Kilo-batches_64) \nDone! Loaded 162 layers from weights-file \ncalculation mAP (mean average precision)... \nDetection layer: 139 - type = 28 \nDetection layer: 150 - type = 28 \nDetection layer: 161 - type = 28 \n332 \ndetections_count = 2537, unique_truth_count = 1017 \nclass_id = 0, name = Person, ap = 75.99% (TP = 453, FP = 169) \nclass_id = 1, name = Shotgun, ap = 91.97% (TP = 40, FP = 3) \nclass_id = 2, name = Handgun, ap = 92.86% (TP = 57, FP = 1) \nclass_id = 3, name = Knife, ap = 96.11% (TP = 80, FP = 2) \nclass_id = 4, name = Rifle, ap = 95.98% (TP = 128, FP = 13) \nfor conf thresh = 0.25, precision = 0.80, recall = 0.75, F1-score = 0.77 \nfor conf thresh = 0.25, TP = 758, FP = 188, FN = 259, average IoU = 63.97% \nIoU threshold = 50%, used Area-Under-Curve for each unique Recall \nmean average precision (
[email protected]) = 0.90582, or 90.58% \nTotal Detection Time: 119 Seconds \nSet -points flag: \n`points 101' for MS COCO \n`points 11' for PascalVOC 2007 (uncomment 'difficult' in voc.data) \n`points 0' (AUC) for ImageNet, PascalVOC 2010-2012, your custom dataset "}],"code_language":"ini"}
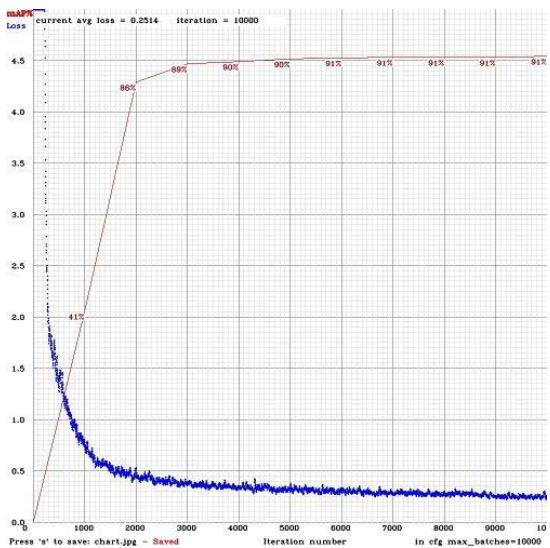
Fig. 3(a): mAP As shown in Fig. 3(b) the model struggled initially with the mean average precision (mAP) of $41.03\%$ for the first 1000. However, over the next 1000 iterations, the performance rose to a significant $86.43\%$.
This improvement is likely due to the exposure of the model to more training data and beginning to understand the features necessary for accurate predictions.

Fig. 4a: Handgun Sample Input Image
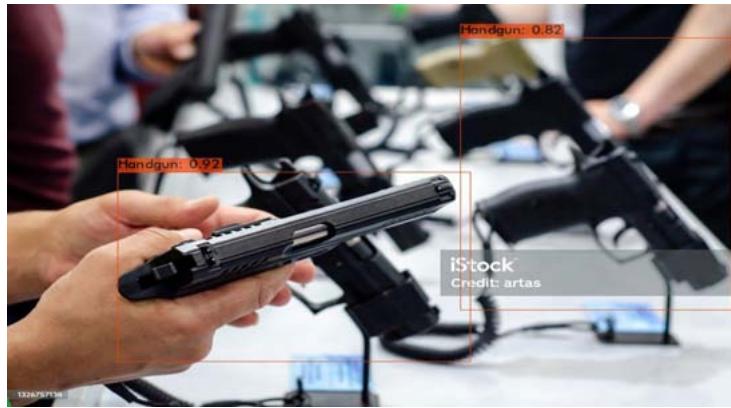

Fig. 4(b): Model Detection Result for Handgun
This assumption was validated as the mean average prediction calculated from 4000 weight and up to 10000th weight maintained an average of $91\%$ mAP. This is shown in Fig. 3b). During this phase, the model already had learned all that is necessary to accurately distinguish, categorize, and predict objects in their various classes. So, the best weight recorded at the $10^{\text{th}}$ saved weight.

Fig. 3(b): Model Performance

Fig. 5(a): Knife Sample Input Image

Fig. 5(b): Model Detection Result for Knife Fig. 6(a): Shotgun Sample Input Image

Fig. 6(b): Model Detection Result for Shotgun For YOLOv4, Table 1 shows the average precision for each of the classes.
Table 1.0: Class AP performance
<table><tr><td>Class Name</td><td>AP (%)</td><td>TP</td><td>FP</td></tr><tr><td>Person</td><td>75.99</td><td>453</td><td>169</td></tr><tr><td>Shotgun</td><td>91.97</td><td>40</td><td>3</td></tr><tr><td>Handgun</td><td>92.86</td><td>57</td><td>1</td></tr><tr><td>Knife</td><td>96.11</td><td>80</td><td>2</td></tr><tr><td>Rifle</td><td>95.98</td><td>128</td><td>13</td></tr></table>
We set a confidence threshold of 0.25 to filter out predictions below this threshold, ensuring a reliable detection mechanism. Notably, the "Person" class achieved an average precision (AP) of $75.99\%$. The model demonstrated strong capabilities in identifying "Person" instances, with 453 true positives (TP) and 169 false positives (FP), suggesting significant improvement from prior iterations following re-annotation and model fine-tuning. The "Shotgun" class (class_id = 1) achieved an AP of $91.97\%$, reflecting its proficiency in detecting such objects. With 40 true positives and 3 false positives, the model exhibited commendable precision and recall for "Shotgun" instances, outperforming its performance in the "Person" class. The "Handgun" class (class_id = 2) showcased even higher accuracy, with an AP of $92.86\%$. The model accurately identified 57 instances of handguns while encountering only 1 false positive, highlighting its ability to discern intricate features of handguns with precision and reliability.
At a detection threshold of 0.25 Table 2.0(a) shows the confusion matrix of the model which shows results of the model's precision, recall, and F1_score while Table 2.0(b) shows results for the True Positive, False Positive, False Negative at a detection counts of 2537 with 1017 unique truth counts.
Table 2.0(a): Confusion Matrix of the Model
<table><tr><td>Precision</td><td>Recall</td><td>F1_Score</td></tr><tr><td>0.80</td><td>0.75</td><td>0.77</td></tr></table>
Table 2.0 (b): Confusion Matrix
<table><tr><td>TP</td><td>FP</td><td>FN</td></tr><tr><td>758</td><td>188</td><td>259</td></tr></table>
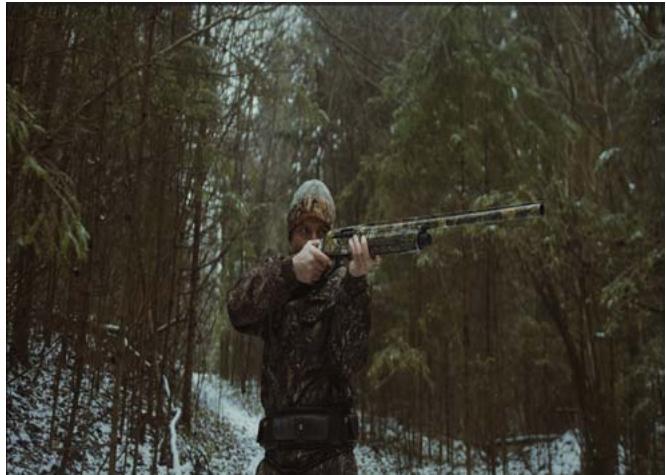

Fig. 7 (a): Crime Video Scenario
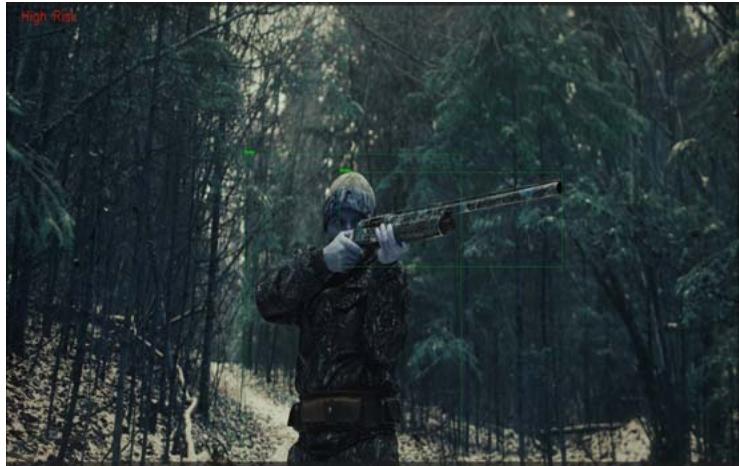

Fig. 7 (b): High-Risk Person Detection and Prediction
Moreover, the model demonstrated the highest accuracy in recognizing "Knife" instances (class_id = 3), achieving an AP of $96.11\%$. With only 2 false positives, the model's 80 true positives underscore its robustness in identifying potential threats posed by knives, significantly contributing to anomaly detection systems. The "Rifle" class (class_id = 4) yielded an AP of $95.98\%$, underscoring the model's exceptional ability to detect rifles. With 128 true positives and 13 false positives, the model demonstrated a remarkable capability to discern criminal scenes associated with rifles, making it an asset in threat detection scenarios. Figures 5a, 6a, and 7a show the input images to our model, while Figures 5b, 6b, and 7b respectively show the results of our model.
The study involves the use of an object detection algorithm for the detection or classification of persons of high risk therefore, we use related detection algorithms to benchmark the performance of this research. In this research when compared with a Yolov4 on UAV imagery, our model performance as shown in Table 1.0 performed greatly, showed superior precisions when compared to the work carried out by [23]; in this related work, the overall mAP was $62.71\%$ with "Person" at $48.67\%$, for the same class in this research we achieved $75.99\%$ mAP. Additionally, an improved YoLov4 model on the S2TLD dataset also from [23] achieved an mAP of overall mAP of $96.98\%$ with classes such as "Red Light" demonstrating an AP as high as $98.15\%$; our model demonstrates its competitiveness with its overall mAP.
## V. CONCLUSION
In conclusion, our research on human tracking and anomaly detection presents a systematic approach to bolstering security and surveillance in complex environments. The primary aim of this research was to readapt an object detection algorithm such as Yolov4 for the detection and classification of crime scenes and use deep learning techniques to identify high-risk individuals based on the objects they possess and actions that they may suggest whether or not they are a person of high risk.
Leveraging a local HP Pavilion gaming machine with specific hardware specifications and a dataset comprising 3317instances from diverse sources, including the UCF crime open dataset. Our model was built on YOLOv4 architecture, it adeptly predicts, and categorizes objects most found in a crime scene, and uses this to predict whether the person holding it is a person of highrisk.
Meticulous annotation and dataset transformation facilitated efficient processing. Despite initial challenges, our model significantly improved, achieving an average precision of $86.43\%$ after 2000 iterations and maintaining $90\%$ from 4000 to 10000 iterations, signifying successful object classification. Table 1 illustrates the model's performance across classes, with notable precision in identifying rifles $(98.90\%)$, handguns $(96.93\%)$, and knives $(97.66\%)$. True positive and false positive values offer insights into accurate instance identification while minimizing misclassifications.
The significance of our findings extends beyond the immediate results. Our model's ability to predict high-risk scenarios is particularly valuable in real-world surveillance applications, providing a robust tool for enhancing security measures. By successfully integrating advanced deep learning techniques, our study contributes to the literature on anomaly detection, especially concerning crime-related behaviors captured in surveillance videos.
However, our study is not without limitations. The dataset, while diverse, may still not cover all possible real-world scenarios, affecting the model's generalizability. Additionally, computational constraints limited the scale of our experiments. Future research could focus on expanding the dataset, improving annotation techniques, and exploring more powerful computational resources to further enhance model performance.
Our study highlights the beauty of our model in predicting high-risk scenarios, particularly in real-world surveillance applications. Advanced deep learning techniques. Our findings contribute to anomaly detection literature, especially concerning crime-related behaviors captured in surveillance videos.
Future improvements could be around expanding the weapons to accommodate contemporary crime-related weapons like bottles, IEDs, etc. Additionally, careful study of criminals must be undertaken to understand the actions underlying the crimes committed, and their nature. For this, an advanced feature extraction could be used to understand actions before a crime.



































































