No ethics committee approval was required for this article type.
Data Availability
Not applicable for this article.
Michelle Jalousie Kommers. 2026. \u201cSocial determinants and COVID-19 vaccination: a study based on global data\u201d. Global Journal of Human-Social Science - F: Political Science GJHSS-F Volume 25 (GJHSS Volume 25 Issue F1): .
## I. INTRODUCTION
A new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus was reported in Wuhan, China, in late December 2019 (He et al., 2020). The most recent evidence supports the hypothesis that SARS-CoV-2 originated from a laboratory leak. Scientific and intelligence reports from 2023 indicated that researchers at the Wuhan Institute of Virology fell ill before the first official case of COVID-19 and that they were handling coronaviruses under biosafety conditions that were below the recommended standards (National Intelligence Council, 2021; Report et al., 2024).
The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 and the resulting global advance of COVID-19 had devastating impacts on multiple spheres of society (Huang et al., 2021). According to data from the World Health Organisation (WHO), between 2020 and 2024, there were more than 201 million cases and more than 3 million deaths related to infection with the virus.
As the pandemic progressed, several strategies were implemented to contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2, including the use of face masks, social distancing, temporary closure of institutions, and the adoption of remote working policies (Murphy et al., 2023). However, these measures have disproportionately impacted low-income populations and communities with a higher proportion of ethnic and social minorities (Sheth & Bettencourt, 2023). This inequality is evidenced in studies that analysed the challenges of access to healthcare during the pandemic, whose results indicated that disparities in access were significantly greater in low- and middle-income countries (Abel et al., 2024).
Much of the narrative constructed during the pandemic maintained that the only hope for a return to normality would be linked to the development of an effective vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 (Torjesen, 2020). For many, the vaccine became a symbol of relief from the continuous cycles of lockdown and the worsening global economic crisis (Al-Jighefee et al., 2021). In this context, a global race was launched to produce the most effective vaccine platform, which resulted in the availability of multiple vaccine technologies throughout the pandemic period.
Despite the rapid development of various vaccine platforms, the population of low-income countries did not have equal access to vaccines and other COVID-19-related treatments (DiRago et al., 2022). A study conducted by De Oliveira et al. (2021) showed that nations with better socioeconomic indicators, such as a higher Human Development Index (HDI), had priority access to vaccination. In general, countries with a high HDI have greater equity in income distribution, which is reflected in better living conditions, access to nutritious food, adequate housing, and basic sanitation — essential factors for maintaining public health.
Consequently, healthier populations tend to be more productive, with greater capacity for work and study, which contributes directly to the economic and social development of these countries (Morse, 2023). This disparity highlights how global structural inequalities have influenced not only the response to the pandemic but also the results in terms of morbidity, mortality, and economic recovery.
To date, there are no studies that comprehensively investigate the relationship between the Human Development Index (HDI) and epidemiological indicators of COVID-19, such as mortality rates and the number of new cases, based on data from global databases. Given this gap, this study proposed to analyse the influence of the HDI and its association with the application of different SARS-CoV-2 vaccine platforms on the number of cases and deaths using two global databases.
## II. METHODOLOGY
This study is retrospective, descriptive, and quantitative. The actions of vaccine programmes worldwide were identified based on information obtained from the World Health Organisation (WHO) via the link https://covid19.who.int/data, and from the Human Development Index (HDI) via the link https://covid19. who.int/data, which has been evaluating countries since 3 January 2020. - HDI) via the link https://hdr.undp. org/data-center/human-development-index#/indices/H DI, evaluated from 03/01/2020 to 02/11/2023. We used eight explanatory variables: HDI, types of vaccines administered, number of cases and number of deaths from COVID-19. It was not possible to analyse the individual effectiveness of the vaccines, as the data provided on the types of vaccines were organised into sets of immunisations administered periodically, forming 143 sets of vaccines.
The research involves only public domain data that does not identify the research participants and does not require approval by the CEP-CONEP System.
### a) Statistical Analysis
In the data obtained, the dates of the vaccines administered by the different countries were allocated and the case and death rates were calculated. For this study, the statistical test used was Mood's median test. This test was chosen because it does not require the data to have a normal distribution or the same sample size. The Mood median test aims to compare the median between two or more groups, adopting a confidence level of $95\%$.
The 'HDI' variable was classified into four categories: very high, high, medium, and low, in order to compare them. To compare the different HDIs, Dunn's statistical test with Bonferroni correction was used, adopting a confidence level of $95\%$ ( $\alpha = 5\%$ ). In this correction, the significance value (p-value) considered for each comparison was adjusted using the formula $\alpha / n$, where $n$ is the total number of comparisons made. For the comparison of vaccines, only graphical methods were used, due to the large number of treatments (variety of vaccines administered per country), which made interpretation using traditional statistical tests unfeasible.
To construct the graphs associated with the treatments, we considered only 20 treatments, 10 of which had the highest medians for case and death rates and 10 of which had the lowest medians for death and case rates. Those in which the median for the death rate and case rate, as well as the confidence interval for them, were equal to zero were excluded from the analysis.
To verify the impact of the number of different vaccines administered on the reduction in case rates and death rates, beta regression was used. Due to the large data set and computational problems in running the analyses, the average of each treatment was used in the regression models. This model was used because the average case and death rates were within the range (0, 1), so the beta regression model with the logit link complement was proposed for the data.
## III. RESULTS
Table 1 shows the degrees of freedom (DF), the test statistic (Chi-square), and the probability value of the Mood test for the variables 'HDI' and 'Vaccine'. The test showed that there is a significant difference at the $95\%$ level for both variables, meaning that there is at least one 'HDI' category and at least one vaccine that differs from the others. At least one of the HDIs showed a significant difference in the number of cases and deaths.
Table 1: Mood Median Test Results
<table><tr><td>Variables</td><td>DF</td><td>Chi-square P-value</td><td>P-value</td></tr><tr><td colspan="4">HDI</td></tr><tr><td>Death rate</td><td>3</td><td>191.2022</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Case rate</td><td>3</td><td>185.3670</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td colspan="4">Treatments</td></tr><tr><td>Death rate</td><td>142</td><td>12683.4409</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Case rate</td><td>142</td><td>12948.6160</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr></table>
Table 2 presents multiple comparisons between HDI and death rates using Dunn's test. For Dunn's test, the null hypothesis is rejected when the p-value is less than $\alpha /6$. According to Table 2, the only groups that did not show a significant difference between them are the
'High' and 'Medium' HDI groups, since the probability value associated with the comparison of both groups was greater than $\alpha / 6$. For the other comparisons, there was a difference.
Table 2: HDI Comparisons for the Death Rate
<table><tr><td>Comparisons</td><td>Z-statistics</td><td>P-value</td></tr><tr><td>High - Low</td><td>3.3317</td><td>0.002</td></tr><tr><td>High - Medium</td><td>-0.7877</td><td>1.000</td></tr><tr><td>Low - Medium</td><td>-3.6552</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>High - Very High</td><td>15.3782</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Low - Very High</td><td>5.1406</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Medium - Very High</td><td>13.4177</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr></table>
Figure 1 shows that countries with a 'Very high' HDI tend to have a lower death rate than countries with other HDI levels. Countries with a 'High', "Medium", and
'Low' HDI have a relatively similar rate that is above the global average.
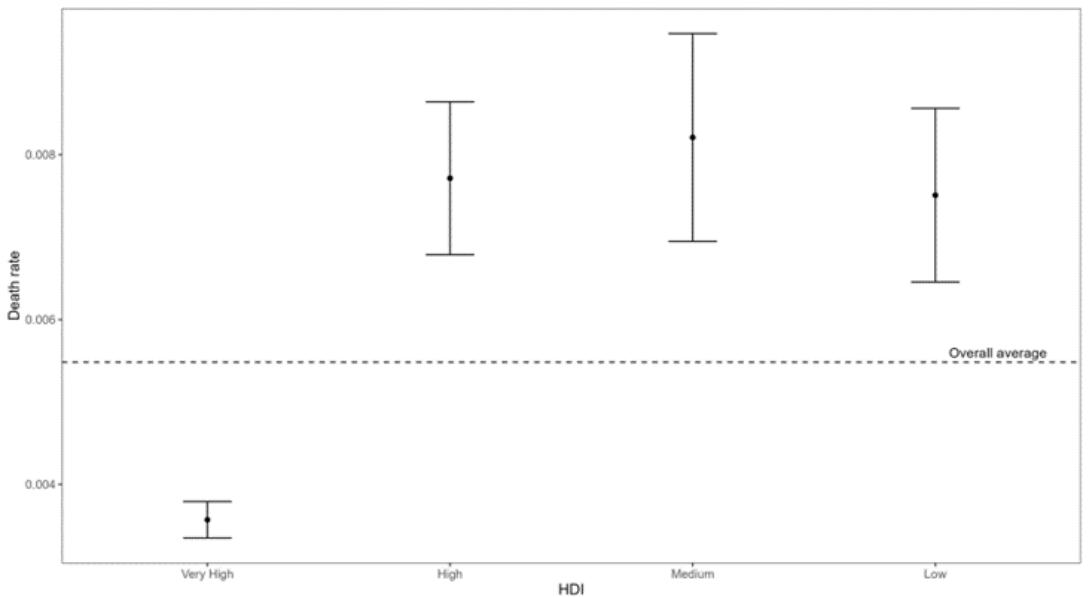 Figure 1: Confidence Interval of the Average Death Rate by Human Development Index
Table 3 presents multiple comparisons for the case index, where the test found no significant difference between the comparisons of 'High' and 'Low' and "Low and 'Medium' HDI, since the probability value for these comparisons was less than $\alpha / 6$.
Table 3: Human Development Index Comparisons for Case Rates
<table><tr><td>Comparisons</td><td>Z-Statistics</td><td>P-value</td></tr><tr><td>High - Low</td><td>2.2883</td><td>0.066</td></tr><tr><td>High - Medium</td><td>5.8970</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Low - Medium</td><td>1.8947</td><td>0.174</td></tr><tr><td>High - Very High</td><td>19.4523</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Low - Very High</td><td>8.5428</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Medium - Very High</td><td>9.2487</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr></table>
Similar to the case of the death rate, countries with very high HDI tend to have a lower case rate, while for other HDIs, there is a slight increase in cases as the HDI level decreases.
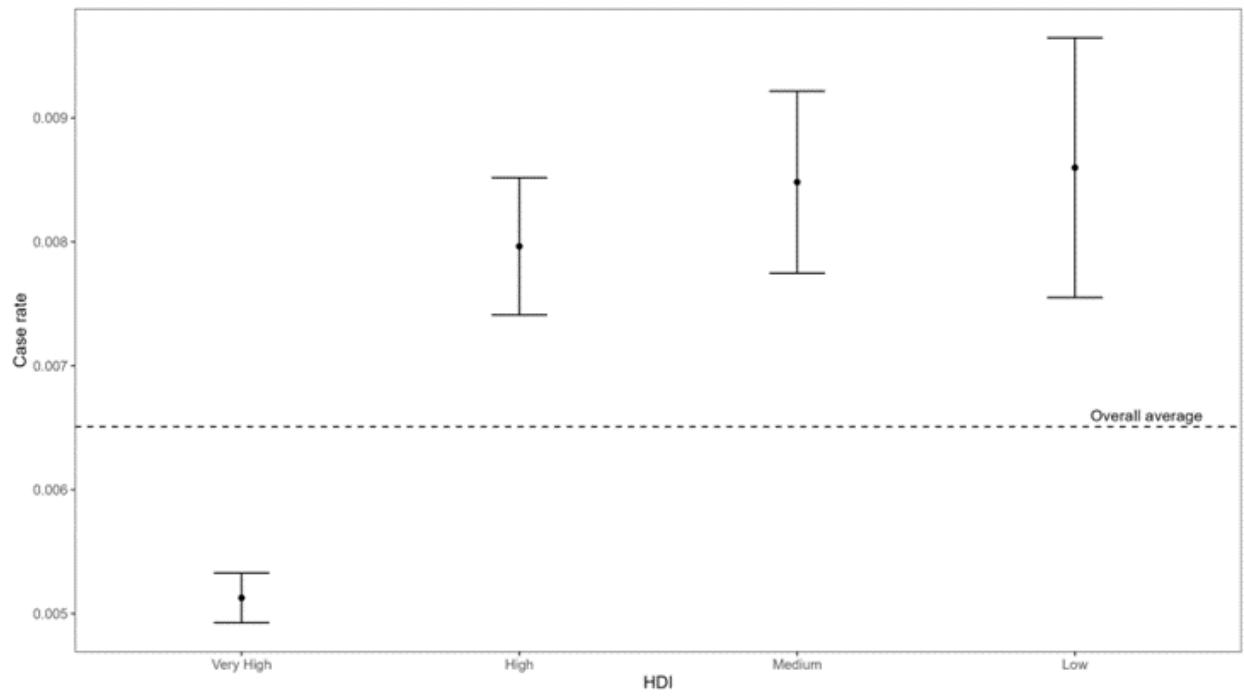 Figure 2: Confidence Interval of the Average Case Rate by Human Development Index As for treatments related to the death rate, treatments 'V124' (Oxford/AstraZeneca; Sputnik V; ZF2001 - Country Uzbekistan - High HDI) and 'V63' (Johnson&Johnson; Oxford/AstraZeneca; Pfizer/BioN Tech; Sinopharm/Beijing; Sinovac - Sudan - Low HDI) had the highest medians and, consequently, death rates (Figure 3). Meanwhile, treatments 'V33' (COVlran Barekat; Covaxin; Oxford/AstraZeneca; Sinopharm/ Beijing; Soberana02; Sputnik V - Country Iran - High HDI), 'V57' (Johnson&Johnson; Moderna; Pfizer/BioN Tech - Country Denmark - Very High HDI), 'V59' (Johnson&Johnson; Oxford/AstraZeneca - Country Jamaica - High HDI) and 'V69' (Johnson&Johnson; Oxford/AstraZeneca; Sinopharm/Beijing - Country Nepal
- Medium HDI) had the lowest death rates. The other treatments shown in Figure 3 had values very close to the overall median (Figure 3).
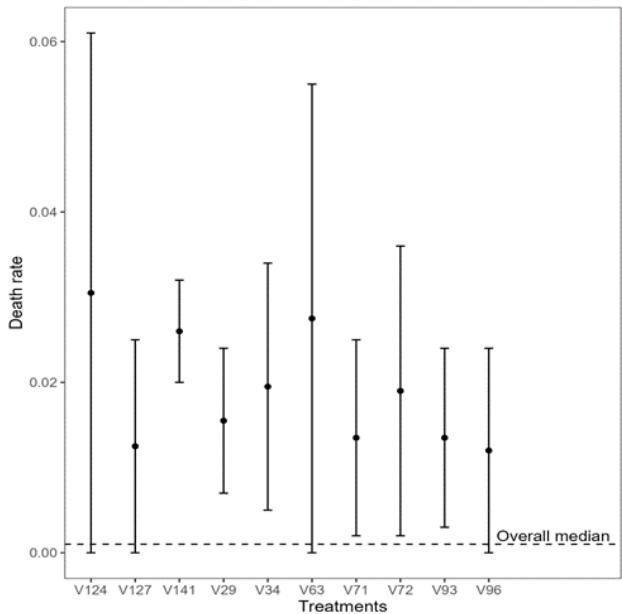
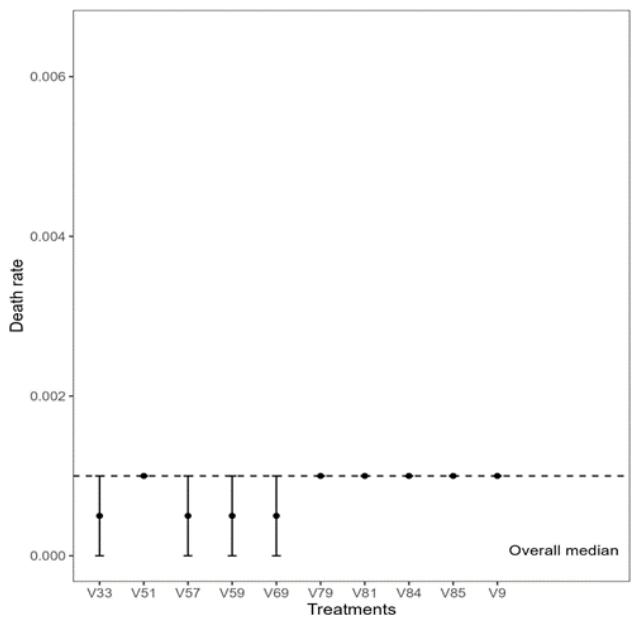 Figure 3: Confidence Interval of the Median Death Rate for the 10 Treatments with the Highest and Lowest Medians (left and right), respectively For the case index, the treatments 'V29' (Covaxin; Oxford/AstraZeneca; Sinopharm/Beijing; Sputnik V – Country Iran – High HDI) and 'V124' (Oxford/AstraZeneca; Sputnik V; ZF2001 – Country Uzbekistan – High HDI) presented the highest median values, i.e., the highest case index. On the other hand, treatments 'V32' (COV/Iran Barekat; Covaxin; FAKHRAVAC; Oxford/AstraZeneca; Razi Cov Pars; Sinopharm/Beijing;
Soberana02; SpikoGen; Sputnik V - Iran - High HDI), 'V41' (Johnson&Johnson; Moderna; Novavax; Oxford/AstraZeneca; Pfizer/BioNTech; Sinopharm/Beijing; Sinovac - Indonesia - High HDI) and 'V59' (Johnson& Johnson; Oxford/AstraZeneca - Jamaica - High HDI) presented the lowest values for the case rate, while the other treatments had very similar values (Figure 4).
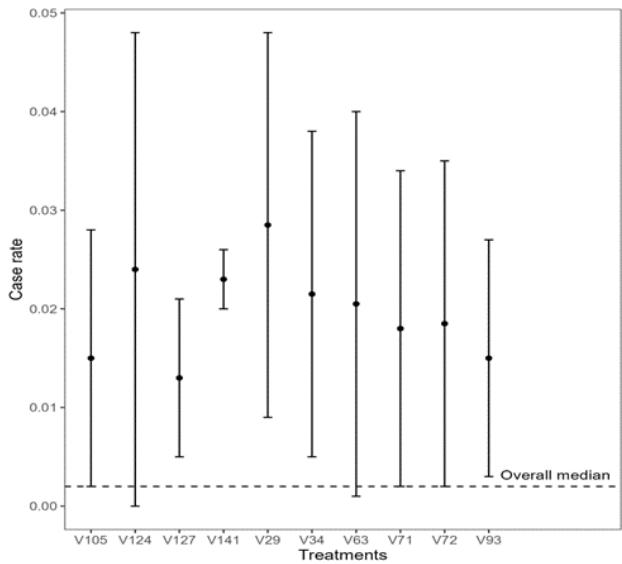
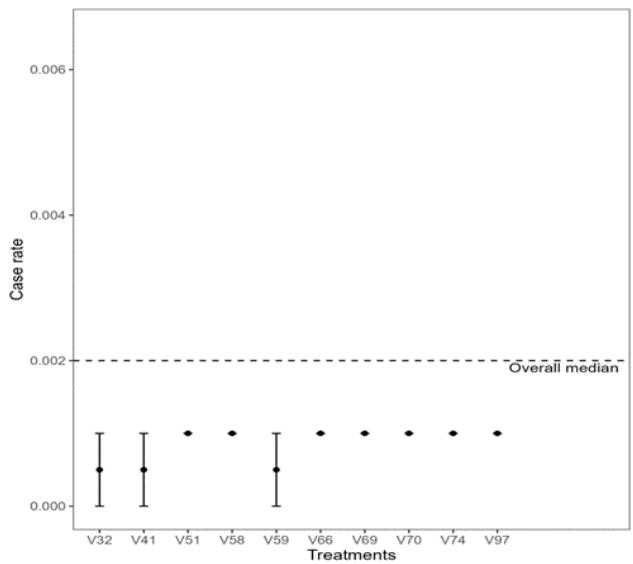 Figure 4: Confidence Interval of the Median Case Index of the 10 Treatments with the Highest and Lowest Medians (left and right), Respectively In Figures 3 and 4, we observe that the application of different vaccine platforms resulted in fewer new cases of COVID-19 patients and fewer deaths. To analyse whether the variety of vaccine platforms applied worldwide was more relevant than one or a few varieties of vaccine platforms, we performed a beta regression model. The dots in the figure represent
the number of countries, and we observe that a few countries used one vaccine platform. We analysed that for each unit increase in the number of vaccines, there is a decrease of approximately $(\exp (-0.0839)\approx 0.9195)$; $(1 - 0.9195)*100\approx 8\%$ in the case index (Table and Figure 5).
Table 5: Parameters of the Beta Regression Model for the Case Index
<table><tr><td>Variable</td><td>Estimate</td><td>Std. Errorz value</td><td>P-Value</td></tr><tr><td>(Intercept)</td><td>-4.2285</td><td>0.1551-27.2702</td><td>< 0.001</td></tr><tr><td>Vaccines</td><td>-0.0839</td><td>0.0352-2.3811</td><td>0.017</td></tr></table>
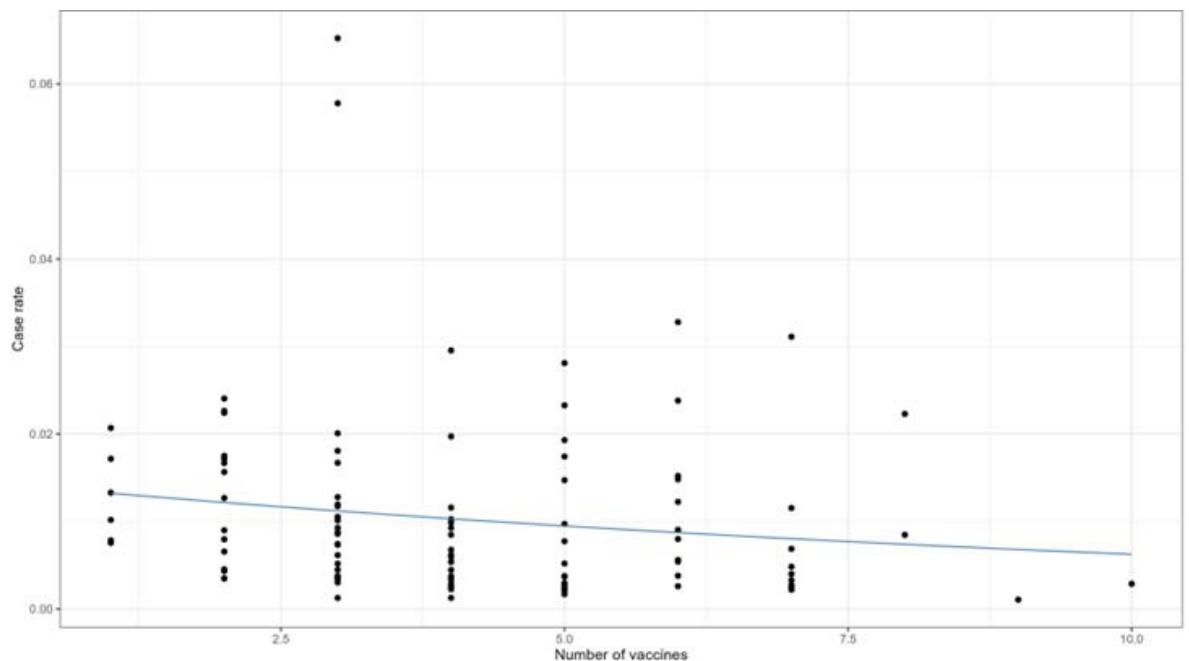 Figure 5: Beta Regression Model for the Case Rate by Vaccine Platform Variety Administered Worldwide
Note: each () represents 1 country analysed.
As for the beta regression model for the death rate, for each increase of one unit in the variety of vaccine platforms, there is a decrease of approximately
$(\exp (-0.1228)\approx 0.8844);(1 - 0.8844)*100\approx 11.55\%$ in the death rate (Table and Figure 6).
Table 6: Parameters of the Beta Regression Model for the Death Index
<table><tr><td>Variable</td><td>Estimate</td><td>Std. Errorz value</td><td>P-Value</td></tr><tr><td>(Intercept)</td><td>-4.1065</td><td>0.1757-23.3685</td><td>0.0000</td></tr><tr><td>Vaccines</td><td>-0.1228</td><td>0.0400-3.0724</td><td>0.0021</td></tr></table>
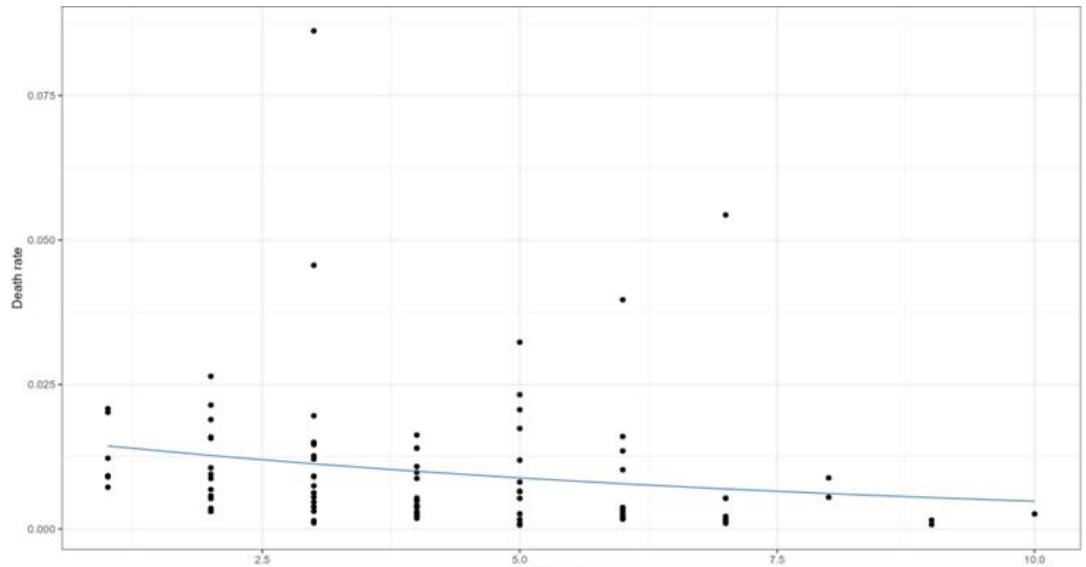 Figure 6: Beta Regression Model for the Death Rate by Vaccine Platform Variety Administered Worldwide
Note: each (.) represents 1 country analysed.
## IV. DISCUSSION
# a) The Importance of HDI in COVID-19 Results
This study demonstrated a relationship between HDI and pandemic outcomes, as it was observed that the population with lower incomes had a higher number of cases and deaths. During the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, the World Health Organisation (WHO) was criticised for allegedly ignoring evidence about the severity of the outbreak and for delaying the declaration of a public health emergency of international concern. The WHO was also accused of failing to investigate violations of the International Health Regulations by countries that imposed travel restrictions, as well as failing to address the human rights implications of strict measures such as quarantines and mandatory isolation (Goetz & Martinsen, 2021; Mao, 2024).
After the pandemic was declared, several countries proclaimed a national state of emergency, which allowed them to take any measures necessary to resolve the crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Since then, governments, leveraging their increased centralised authority to control the reproduction rate of the new coronavirus, have progressively announced various measures that have closed schools and universities, public spaces, non-essential businesses and economic activities, along with restricting the movement of individuals (colloquially referred to as 'lockdown' or isolation) (Ferraresi & Gucciardi, 2022; Murphy et al., 2023). All these measures came into force in the same way in all territories (Ferraresi & Gucciardi, 2022; Murphy et al., 2023).
As a result of this decision, communities with higher proportions of minority populations, immigrants, workers, and low-income wage earners suffered from job losses, limited access to health services and information, as well as high rates of cases and deaths (Sheth & Bettencourt, 2023). For example, the mortality rate ranged from 121.2 per 100,000 inhabitants (95% CI: 112-131) in the highest income quartile to 150.2 (95% CI: 136-165) in the lowest income and most disadvantaged quartile in the city of Barcelona. The hypothesis is that quarantine measures increased health inequalities, especially among the most disadvantaged groups (Politi et al., 2020). In this sense, it is very likely that increased exposure among members of large families is associated with other factors, including poor housing quality or inadequate disinfection measures. In a review of stay-at-home orders, the authors concluded that there was a relatively small additional effect on virus transmission, with variable mortality rates. With the closure of schools, minimal transmission was observed (Murphy et al., 2023).
Sweden's unique approach to pandemic management, which avoided lockdowns and mandatory vaccination, also attracted attention. Despite these flexible measures, Sweden had one of the lowest COVID-19 mortality rates in Europe, and the long-term impact on excess mortality was similar to that of other Nordic countries that adopted stricter lockdown approaches (Hallberg et al., 2025). This atypical case suggests that, in addition to vaccination, other factors such as public behavior, the resilience of the healthcare system, and perhaps the development of herd immunity, play a significant role in the pandemic's outcomes (Kubai, 2022). For example, high levels of trust in government and adherence to voluntary guidelines may have contributed to Sweden's relatively favourable outcomes (Born et al., 2021). As such, caution should be exercised when drawing consensus conclusions from WHO data alone, and a more nuanced analysis is needed to understand the interaction of various factors.
Most cases of cluster transmission in China occurred in large families living together in crowded homes, a common profile in low-income communities (WHO & Aylward, Bruce (WHO); Liang, 2020). In addition, the mortality rate from COVID-19 was higher among populations with underlying chronic diseases (Abduljalil & Abduljalil, 2020; Adhikari et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2021). A Finnish multicohort study has consistently shown that unfavourable socioeconomic status is associated with a higher prevalence of chronic diseases, including heart disease, obesity, and diabetes (Kivimäki et al., 2020).
Brazil, the largest country in South America, clearly reflects the socioeconomic disparities between its federal units. According to a study that evaluated 14 variables, the factors most closely related to the number of cases and deaths from COVID-19 in Brazilian states were: the influenza vaccination rate, the number of intensive care beds, the number of ventilators, the number of doctors and nurses, and the HDI, with a positive correlation according to Spearman's correlation test (Galvan et al., 2020). Consequently, the lowest rates of cases and deaths from the disease were recorded in states with the highest rates of influenza vaccination, intensive care beds, ventilators, doctors and nurses per 100,000 inhabitants, which consequently have some of the highest HDI in the country (Galvan et al., 2020). In summary, these results reinforce the idea that regions or countries with better financial conditions have lower rates of cases and deaths, not only because they provide the vaccine, but also because they provide better resources and infrastructure to combat the disease.
Interestingly, in another continental analysis of disease cases, Oceania and Africa had a very low rate of cases per million inhabitants. According to the authors, the low number of cases in Africa seems to have been caused by the reduced number of tests performed on this continent, while Oceania performed the highest number of tests per thousand inhabitants (Zahid & Perna, 2021). Another ecological profile study reached similar conclusions, showing that the higher the HDI, the higher the cumulative incidence rate of cases, the cumulative incidence rate of deaths, and the number of tests performed (Mirahmadizadeh et al., 2022). This correlation may be due to the strong infrastructure of countries with higher HDI, which allowed them to perform more laboratory tests, thanks to their greater purchasing power for tests and other materials. The high incidence in nations with higher HDI may also be linked to the effectiveness of their health systems in terms of early identification and detection of asymptomatic and subclinical diseases, as well as the implementation of more effective screening programmes (de Oliveira et al., 2021; Mirahmadizadeh et al., 2022). The studies mentioned only reinforce the socioeconomic discrepancy between countries and continents, as well as the possible underreporting of data on COVID-19 morbidity and mortality in low-income countries.
The pandemic has had a significant impact on China, the European Union and the United States, causing global political centres to place this issue at the forefront of their concerns (Bangalee & Suleman, 2020). As a result, countries such as the United States, Canada, Germany and some in the European Union have proposed investing more than $1 billion in public funds for research, vaccine development, diagnostics and other promising therapies for COVID-19. This led governments to finance the construction of factories to produce vaccines and other essential materials, as well as to purchase products that did not previously exist in marketable form, thereby facilitating access to treatment for this population (Bangalee & Suleman, 2020; Guimarães, 2020). This may explain why countries with higher development indices had lower mortality rates, especially when the disease immunisation policy began to be implemented. In another study, we found that countries with better socioeconomic indicators, such as higher life expectancy and higher HDI, had access to the best treatments against COVID-19, priority vaccination and better population coverage (de Oliveira et al., 2021; Ning et al., 2022).
For example, in August 2020, the United States government had invested up to $9 billion in 19 COVID-19 vaccine candidates, distributed among seven companies (Shao, 2024). In this context, the United Kingdom and the United States of America ordered large quantities of COVID-19 vaccine candidates before their approval by regulatory bodies (Shao, 2024). The total number of vaccines pre-ordered by governments would have a certain redundancy in order to guarantee access to the first batches and speed up the manufacturing process. In other words, there was no certainty that any particular vaccine would be successful or when it would be available; therefore, instead of betting on just one vaccine, the richest countries invested in several vaccine platforms, which would offset the cost of the failure of a particular vaccine (Torjesen, 2020).
The countries that received the largest quantities of vaccine doses were as follows (in millions): United States (59,585), China (40,520), United Kingdom (17,465), India (10,715), and Israel (7,132). As of 19 February 2021, 80 countries $(42.1\%)$ had already received a batch of COVID-19 vaccines. The first countries to gain access to the vaccine against the disease were the United Kingdom (68 days), China (68 days), Russia (66 days), Israel (62 days), the United States of America (61 days) and Bahrain (58 days). Countries that had already vaccinated their populations showed better socioeconomic indicators (de Oliveira et al., 2021).
Higher-income countries contributed their efforts in terms of resources, funding, and partnerships with other countries. For example, the United States' contribution to the COVID-19 Vaccine Global Access Initiative (COVAX), led by the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (GAVI), the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), and the WHO, was instrumental in accelerating the distribution of vaccines worldwide (Acharya et al., 2021). However, despite the participation of many high-income countries in COVAX, they continued to prioritise bilateral agreements directly with vaccine manufacturers, which resulted in a shortage of vaccines for COVAX (de Oliveira et al., 2021; Ning et al., 2022; Pratama, 2023; Shao, 2024).
### b) Impact of Vaccine Platforms
Analysis of vaccination treatments revealed notable variations in their effectiveness, which can be attributed to factors such as vaccine type, administration strategies, and the health status of different populations. Treatments implemented in countries with a 'very high' HDI, such as the widespread use of Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, and Pfizer/BioNTech brands (see Figures 3 and 4), were associated with lower mortality rates. This highlights the importance not only of vaccine availability but also of the efficiency of health systems in administering and monitoring these treatments. According to De Oliveira et al. (2021), a country with a 'very high' HDI may have better vaccine storage and distribution logistics, ensuring their integrity, as well as more effective public health campaigns to encourage vaccination, leading to higher vaccination rates and better protection globally.
It is important to note that most countries used more than two vaccine platforms. However, this study was not designed to evaluate the effectiveness of the vaccine against coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), as the information obtained is based on published and observed data that may have been affected by underestimation problems and is insufficient to draw any conclusions about effectiveness.
Given the vaccine development process, governments had to invest in a diversified portfolio to maximise the chances of discovering a successful and effective vaccine as quickly as possible (Shao, 2024). A vaccine based on a single platform may work better for certain groups due to its safety profile, method of administration, stability during transport, or because it is faster to produce and requires a simpler manufacturing process (Verdecia et al., 2021). As a result, the industry's multi-platform approach has helped to contain some of the inequality.
In our study, it was not possible to determine which vaccine platform was most effective, as the WHO database consists of a series of vaccine platforms applied in countries, most of which administered three or more platforms, reaching a total of ten in the same time frame. This aspect makes it impossible to analyse the most efficient vaccine platform, and the database does not provide us with information on mild and severe adverse events that occurred in the post-vaccination period.
Some studies have investigated the comparison between homologous and heterologous vaccines in terms of morbidity and mortality. In a cohort study conducted in four Nordic countries, the authors concluded that heterologous vaccination was superior by $27.2\%$ for the AZD1222+BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 regimens and $23.3\%$ for the BNT162b2+mRNA -1273 regimens in terms of preventing hospitalisations due to COVID-19, and by $21.7\%$ and $18.4\%$ in terms of preventing deaths due to the disease, respectively (Andersson et al., 2023). Alternative heterologous COVID-19 vaccinations showed, in a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, antibody response rates and vaccine efficacy equivalent to homologous regimens in immunocompromised individuals (Pardo et al., 2024).
On the other hand, a systematic review with meta-analysis and sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials suggests that heterologous booster vaccines may not be effective in reducing all-cause mortality compared to homologous booster vaccines (RR 0.86; $95\%$ CI: 0.33-2.26; $I^2$ $0.0\%$ ) (Asante et al., 2024). In addition, the association between adrenal crisis and COVID-19 vaccination has been suggested with the possible risk of heterologous vaccination (Maguire et al., 2023; Markovic et al., 2022). Another study, which aimed to investigate psychiatric adverse events after vaccination against the disease in question in a large population cohort in Seoul, South Korea, showed an increased risk of anxiety, dissociative disorders, stress-related disorders, and somatoform and sleep disorders, which were intensified by heterologous vaccination (Kim et al., 2024).
However, few clinical trials have been developed to date to confirm these results. Recently, a phase III clinical trial was conducted in Brazil that applied three different vaccine platforms against the disease (recombinant protein - SCB-2019, Clover; adenovirus vector - ChAdOx1-S, AstraZeneca/Fiocruz; or mRNA - BNT162b2, Pfizer/Wyeth) in adults who had previously received a full series of different vaccines, with no, one or two previous booster doses. Seven serious adverse events were reported (epileptic seizure, cholelithiasis, upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage, acute myocardial infarction, appendicitis, ophthalmic herpes zoster, and abortion) between 9 and 93 days after the booster dose in all participants vaccinated in this study (Clemens et al., 2024).
The CDC pointed out that evidence suggests that, although rare, these events are linked to certain types of COVID-19 vaccination. For example, myocarditis was observed more frequently in male adolescents and young adults, up to seven days after the second dose of the messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine against COVID-19. Cases have also been observed in women, in other age groups, and after other doses of the vaccine (CDC, 2025; Goddard et al., 2022; Kralalik et al., 2022; Montgomery et al., 2021; Weintraub et al., 2022; Wong et al., 2022).
Based on data from the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), the rate of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) in the first 21 days after administration of the J&J/Janssen vaccine was 21 times higher compared to the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna (mRNA) vaccines. After the first 42 days, the rate of GBS was 11 times higher after administration of the J&J/Janssen vaccine. The same study did not identify an increased risk of GBS after administration of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna vaccines (Abara et al., 2023; CDC, 2025). Based on these data, the Advisory Committee on Immunisation Practices (ACIP) recommended the administration of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 instead of the J&J/Janssen vaccine, which, for the reasons already mentioned, has not been available in the United States of America since May 2023 (CDC, 2025).
It is important to note that, despite the identification of some serious adverse effects (Polack et al., 2020), the WHO strongly recommended vaccination in high-risk populations, arguing that although mild to moderate adverse effects were common, serious or long-lasting adverse events remained rare (WHO, 2022). However, the AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine is no longer being produced, and its marketing authorisations were withdrawn in the European market in March 2024 and worldwide in May of the same year, following reduced demand, months after the company admitted in court documents that the vaccine can cause a rare and serious side effect. Cases of serious conditions, such as transverse myelitis and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), have been reported, particularly among younger women (Dugar et al., 2024; Mendick, 2024).
### c) Study limitations
We did not obtain additional information from the global database on the efficacy and mild and serious adverse events of the vaccines administered, nor on the profile of the patients. According to the WHO (2022), each country was responsible for developing a plan to introduce COVID-19 vaccination and implementing the risk management plan recommended by the national regulatory authority, including enhanced active and passive surveillance (adverse events of special interest) throughout the country. We emphasise that countries with low HDI may have underreported information due to insufficient technological infrastructure. The lack of further information on the results of vaccine administration on the WHO platform is related to limited access to global data.
### d) Final Remarks
In general, more rigorous and independent clinical trials are needed to understand the interaction between immunity, vaccine efficacy, and public health strategies. This is because it was not possible to evaluate the efficacy of each vaccine platform individually, since the global database included several sets of vaccine platforms applied during the time interval analysed. Future research should seek to integrate these various elements to form a comprehensive understanding of how to develop effective and equitable responses to global health crises, taking into account both the socioeconomic context and the specific characteristics of each population.
## V. CONCLUSION
This study provided significant insight into the intricate relationship between HDI, the application of various vaccine platforms, and pandemic outcomes, focusing specifically on mortality and case rates. Understanding this dynamic is crucial to informing public health strategies and resource allocation during pandemics, enabling more targeted and effective interventions.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that no sponsorship could have influenced the results.
### ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Although this study was not sponsored or funded, we would like to thank the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) for the scholarship granted.
Our website is actively being updated, and changes may occur frequently. Please clear your browser cache if needed. For feedback or error reporting, please email [email protected]
×
This Page is Under Development
We are currently updating this article page for a better experience.
Thank you for connecting with us. We will respond to you shortly.