This study investigates the influence of relational social capital focusing on trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification on innovation performance among Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) within Nigeria’s textile manufacturing sector. Operating in a resource-limited environment, these MSMEs face unique challenges that make relational social capital a critical asset for sustaining competitive advantage and fostering innovation. Using a mixed-method approach, data was obtained from 564 respondents, we integrate Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA) to capture both linear and configurational effects of relational social capital. Results from PLS-SEM reveal that identification significantly enhances innovation performance, while other elements like trust, norms of cooperation and reciprocity exert varied influences. Further, fsQCA identifies five unique configurations of relational social capital elements contributing to high innovation performance, highlighting the essential role of identification alongside specific relational dynamics.
## I. INTRODUCTION
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a crucial role in driving economic growth, employment, and innovation, particularly in developing economies. In Nigeria, MSMEs contribute approximately $48\%$ to the national Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and account for over $80\%$ of employment, underscoring their significance in poverty alleviation and economic empowerment (PwC, 2020; World Bank, 2021). These enterprises are not only engines of job creation but also act as catalysts for inclusive economic progress by extending opportunities to both urban and rural areas. Their flexibility enables them to adapt swiftly to changing market conditions, which is essential for resilience and innovation (OECD, 2017; Ayyagari, Demirguc-Kunt, and Maksimovic, 2014). However, despite their importance, MSMEs especially those in developing countries face significant challenges that constrain their innovation performance and growth. In developing economies like Nigeria, MSMEs encounter obstacles such as limited access to finance, inadequate infrastructure, and weak formal networks for knowledge and resource sharing (Ayyagari et al., 2014; Beck, Demirguc-Kunt, and Levine, 2005). Access to funding remains one of the most critical issues, as financial institutions often regard MSMEs as high-risk investments due to insufficient collateral and limited financial documentation (Beck and Demirguc-Kunt, 2006). This lack of financial access restricts MSMEs' ability to invest in innovative practices, which are essential for remaining competitive in a globalised economy (OECD, 2017). Consequently, MSMEs increasingly rely on alternative, non-monetary resources to support their innovation efforts, with social capital emerging as a key resource. Social capital, defined as the network of relationships that provide access to information, resources, and support, plays an essential role in facilitating innovation for MSMEs operating in resource-limited environments (Adler and Kwon, 2002; Putnam, 2000).
Social capital, broadly classified into structural, cognitive, and relational dimensions, is increasingly recognized as a driver of innovation, particularly for MSMEs (Nahapiet and Ghoshal, 1998; Coleman, 1988). Structural social capital refers to the overall configuration of ties within a network, which allows for resource sharing and information flow. For MSMEs, a well-connected network can provide access to nonredundant information, which is critical for identifying market opportunities and accessing diverse perspectives (Burt, 2000; Tsai, 2001). Cognitive social capital encompasses shared values, goals, and understandings within networks, which promote alignment and support collaborative innovation efforts (Chiu et al., 2006; Putnam, 2000). Cognitive alignment reduces friction in collaborative projects, enabling smoother interactions and facilitating reciprocal knowledge exchanges essential for innovation (Nahapiet and Ghoshal, 1998; Reagans and McEvily, 2003).
Relational social capital the focus of this study refers to the quality of interpersonal connections within a network, including trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification (Coleman, 1988; Granovetter, 1985). Relational social capital shapes the depth and strength of resource-sharing relationships and is particularly relevant for MSMEs in resource-limited settings, where access to formal resources is scarce (Uzzi, 1997; Adler and Kwon, 2002). Trust, a cornerstone of relational social capital, reduces perceived risks and enables MSMEs to engage in open exchanges of knowledge and resources without the need for formalised agreements (Levin and Cross, 2004). In addition, norms of cooperation encourage collective action, facilitating joint problem-solving and resource pooling, which are essential for overcoming individual resource constraints (Coleman, 1988; Moran, 2005). Reciprocity ensures sustained, balanced exchanges within networks, fostering a reliable flow of support and resources that bolsters innovation (Putnam, 2000; Tsai and Ghoshal, 1998). Finally, identification strengthens the network's cohesion by fostering a shared sense of belonging and commitment to collective goals, enhancing cooperation and alignment (Nahapiet and Ghoshal, 1998).
Prior literature on relational social capital and MSME innovation performance is derived from studies conducted in developed economies, where MSMEs typically operate within well-structured institutional frameworks and have access to formal resources (Adler and Kwon, 2002; Beck et al., 2005). The dynamics of relational social capital in developing economies like Nigeria, where MSMEs encounter distinct socioeconomic challenges, remain underexplored. For instance, cultural factors in Nigeria may shape norms of obligation and reciprocity differently, influencing how MSMEs interact, share resources, and support each other (Ayyagari, Demirguc-Kunt, and Maksimovic, 2014). Addressing this contextual gap is essential for understanding how relational social capital operates under the unique conditions faced by resource-constrained MSMEs that rely heavily on informal networks for growth and innovation.
This study seeks to address significant theoretical gaps by examining the configuration-specific and context-dependent effects of relational social capital on MSME innovation performance. While previous research has often treated relational social capital as having a uniform effect on innovation, emerging perspectives suggest these effects are likely configuration-dependent. Specific combinations of relational elements such as trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification may interact uniquely to produce varied innovation outcomes (Tsai and Ghoshal, 1998; Ragin, 2008). For example, trust may have a stronger impact on innovation when combined with high reciprocity, while its effect might differ if paired with weaker norms of cooperation. Such configuration-specific studies are rare in MSME literature, especially regarding innovation in developing economies (Ragin, 2008; Granovetter, 1985).
To explore these relationships, this study employs a complementary methodology of Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA). This approach captures the complex, non-linear relationships between relational social capital elements and MSME innovation performance, offering a multifaceted perspective that accounts for the conditional and context-dependent effects of relational social capital in resource-limited MSMEs (Burt, 2005; Granovetter, 1983). Additionally, this research contributes to the underrepresentation of MSMEs in developing economies within the social capital literature by providing empirical evidence from Nigeria, supporting a contextualised understanding of relational social capital's role in driving MSME innovation performance (Levin et al., 2016).
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents a literature review together with the hypothesis development. Section 3 details the research methodology. Section 4 present the data analysis and findings of the PLS-SEM. Section 5 present the data analysis and findings of the fsQCA. Section 6 concludes the study by summarising the discussions and conclusion, implications, limitations and future research.
## II. LITERATURE REVIEW
### a) Overview of Social Capital Theory
Social capital theory suggests that relationships and social networks provide valuable resources that individuals and organisations can use to achieve shared goals and mutual benefits. This concept was initially framed by Bourdieu (1986), who viewed social capital as the sum of resources that individuals or groups can access by virtue of their social networks. Social capital was later expanded by Coleman (1988), who emphasised its role in facilitating cooperative action, particularly within communities where formal regulatory systems are weak. Coleman argued that social capital is embedded within social structures, enabling individuals and organisations to collaborate more effectively by reducing transaction costs, fostering trust, and facilitating the flow of information.
Putnam (2000) further developed the concept by focusing on the community level, distinguishing between bonding and bridging social capital. Bonding social capital refers to the strong ties within homogeneous groups, promoting loyalty and trust, while bridging social capital pertains to weaker ties that connect diverse groups, enabling the exchange of novel information and perspectives (Putnam, 2000). While bonding capital is crucial for solidarity, bridging capital has been shown to enhance innovation by providing access to a wider array of resources and ideas, particularly valuable for organisations operating in resource-constrained environments (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998; Adler & Kwon, 2002).
Scholars generally categorise social capital into three dimensions structural, cognitive, and relational, each contributing uniquely to network dynamics and outcomes.
Structural social capital refers to the configuration of the network, including the presence and strength of ties between actors (Burt, 2000). Networks with strong structural social capital enable members to access unique resources and non-redundant information, which can foster innovation (Burt, 1992; Tsai, 2001). Burt's theory of "structural holes" highlights how organisations positioned between disconnected groups can leverage their intermediary status to gain access to diverse knowledge, which is particularly relevant for MSMEs seeking to compete in dynamic markets. However, Burt (2005) also warns that an overreliance on structural social capital can lead to a focus on maintaining advantageous positions rather than engaging in deep, reciprocal exchanges, which can stifle trust and collaboration.
Cognitive social capital encompasses shared goals, values, and languages that facilitate understanding and alignment within networks (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998). When members of a network share similar perspectives and objectives, they can collaborate more smoothly, minimising conflicts and miscommunications (Chiu et al., 2006). Cognitive alignment is particularly beneficial for innovation within MSMEs, as it fosters a shared sense of purpose and reduces the costs associated with coordinating diverse activities (Chumnangoon, Chiralaksanakul, and Chintakananda, 2023). However, a high degree of cognitive social capital may also limit innovation by encouraging conformity and reducing exposure to novel ideas, which can be essential for breakthrough innovations (Levin & Cross, 2004). Therefore, while cognitive alignment supports effective collaboration, it must be balanced with openness to external perspectives to prevent groupthink (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998).
Relational social capital is concerned with the quality of interpersonal relationships within a network, specifically through elements like trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification (Coleman, 1988; Granovetter, 1985). Trust plays a foundational role, reducing perceived risks and encouraging open exchanges of knowledge and resources, which are critical for fostering innovation in MSMEs that often operate with limited formal protections (Levin & Cross, 2004; Uzzi, 1997). Trust and cooperation within relational social capital enable organisations to pool resources and collaborate on complex projects, driving innovation while lowering the transaction costs associated with formal contracts (Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998; Moran, 2005). However, while high levels of relational social capital support stability and cohesion, they may also create network insularity, where members become overly reliant on familiar partners and are less likely to seek external perspectives, potentially stifling innovation (Burt, 2005; Garcia-Morales et al., 2014).
Social capital's implications for MSMEs are profound, as these businesses often lack the resources to develop independent competitive advantages. For MSMEs, social capital provides access to external resources, markets, and knowledge, compensating for internal limitations and allowing them to innovate and grow (Vu, Binh, and Duong, 2023). Empirical studies indicate that MSMEs with robust social capital can better access financing, form strategic partnerships, and navigate market uncertainties, giving them a competitive edge over isolated firms (Nguyen and Canh, 2021). However, excessive reliance on social capital can be detrimental if it restricts the flow of fresh ideas, as network homogeneity may lead to complacency and limit the firm's ability to adapt to changes (Adler & Kwon, 2002).
While social capital is a valuable asset that enhances MSME innovation and resilience, it requires careful management. Structural social capital offers access to unique resources but may limit deep collaboration. Cognitive social capital facilitates smooth interactions and shared understanding but can hinder creative thinking if overemphasised. Relational social capital promotes trust and reciprocal support but risks network insularity if not balanced with diverse external connections. For MSMEs, achieving an optimal mix of these dimensions is crucial to leveraging social capital effectively for sustained innovation and growth in competitive markets (Vu, Binh, and Duong, 2023; Nguyen and Mort, 2022).
### b) Relational Social Capital and MSME Innovation Performance
Relational social capital, with its focus on trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification, is essential for driving innovation within MSMEs, especially in resource-limited environments (Adler & Kwon, 2002; Granovetter, 1985). These elements collectively promote collaboration, knowledge sharing, and resource exchange within networks, which enhances MSMEs' innovative capabilities.
Trust facilitates open exchanges by minimising perceived risks and reducing the need for formal agreements, allowing MSMEs to share information freely (Roxas, 2007). Trust-based networks enable MSMEs to access diverse knowledge sources, fostering collaborative and flexible innovation. For instance, Santos,
Oliveira, and Curado; 2023 found that trust among small businesses facilitated adaptation and responsiveness to market changes, illustrating trust's role in innovation. However, high levels of trust can lead to network insularity, where firms become overly dependent on familiar partners, limiting exposure to new ideas essential for radical innovation (Burt, 2005; Granovetter, 1985).
Norms of Cooperation within relational social capital encourage MSME network members to prioritise collective goals, which supports joint problem-solving and resource pooling (Coleman, 1988; Moran, 2005). In cooperative environments, MSMEs can overcome individual resource limitations by combining expertise and resources, fostering synergies that enhance creativity (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998). In resource-constrained settings, such as developing economies, cooperative norms are particularly valuable, allowing MSMEs to achieve more substantial innovation outcomes together than they could individually (Aldrich & Kim, 2007). However, too much emphasis on cooperation can sometimes suppress individual initiative, potentially reducing the diversity of innovative approaches within the network (Inkpen & Tsang, 2005).
Reciprocity establishes balanced, sustained exchanges within networks, creating an environment where MSMEs can depend on consistent support for innovation (Putnam, 2000). This mutual assistance cycle encourages network members to contribute resources and knowledge with an understanding that support will be reciprocated, enhancing the network's resilience and innovation capacity (Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). Research indicates that reciprocal exchanges are crucial for MSMEs in resource-limited contexts, providing a reliable source of support that enables continuous innovation (Molm, 2003; Pham et al., 2020). However, reciprocity can sometimes lead to imbalances if some network members contribute more than others, which may strain relationships over time (Molm, 2003).
Identification within relational social capital fosters a shared sense of belonging and loyalty among MSME network members, encouraging them to prioritise the network's collective goals over individual interests (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998). Identification strengthens cohesion, motivating members to support each other's innovation efforts by pooling knowledge and resources more willingly (Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). In resource-constrained environments, identification helps MSMEs work cohesively toward common objectives, enhancing their ability to innovate collectively. However, excessive identification can lead to over-alignment, where members may overlook external perspectives and limit the diversity needed for breakthrough innovations (Adler & Kwon, 2002; Granovetter, 1985).
### c) Hypothesis Development
This study investigates how different components of relational social capital trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification contribute to innovation performance within MSMEs. Relational social capital plays a critical role in resource-limited contexts, enabling MSMEs to overcome constraints through collective strategies that drive innovation (Adler & Kwon, 2002; Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). Each of these components is hypothesised to impact MSME innovation positively by fostering an environment of shared knowledge, cooperation, and mutual support, thus enhancing both incremental and breakthrough innovations.
## i. Trust within Relational Social Capital
Trust is a foundational aspect of relational social capital, creating a secure environment where network members feel comfortable sharing knowledge and resources without fear of opportunistic behaviour (Coleman, 1988; Levin & Cross, 2004). Trust reduces transaction costs and facilitates open communication, making it particularly valuable for MSMEs that may lack formal protections like patents or legal safeguards (Zahoor and Gerged, 2023). Research by Tsai and Ghoshal (1998) emphasises that trust within a network reduces the perceived risks associated with knowledge sharing, enabling members to draw upon diverse knowledge sources that can lead to creative and innovative solutions. For MSMEs, trust supports collaborative problem-solving and rapid adaptation to changing market conditions, allowing firms to leverage network knowledge for sustained innovation (Santos, Oliveira, and Curado, 2023; Shi, Shepherd, and Schmidtts, 2015). Therefore, we hypothesise that trust within relational social capital positively influences MSME innovation performance by fostering a safe and open environment for knowledge exchange.
H1: Trust within Relational Social Capital has a Positive Effect on MSME Innovation by Enabling Safe Knowledge Sharing
## ii. Norms of Cooperation in Relational Social Capital
Norms of cooperation represent shared expectations within networks that prioritise collective over individual interests, fostering a culture of mutual support (Coleman, 1988; Moran, 2005). In MSMEs, cooperative norms encourage members to pool resources and expertise, creating synergies that help overcome individual limitations and drive innovation (Santos, Oliveira, and Curado, 2023). Studies suggest that cooperative norms in relational social capital allow MSMEs to engage in joint problem-solving and collaborative innovation, especially in contexts where financial and technical resources are limited (Kim and Shim, 2018; Roxas, 2007). Cooperative networks enable MSMEs to tackle complex challenges by accessing a broader base of knowledge and resources, which enhances their ability to generate innovative solutions and respond to market demands (Onofrei et al., 2020). Thus, we hypothesise that norms of cooperation within relational social capital positively impact MSME innovation by facilitating collective efforts toward resource pooling and collaborative problem-solving.
H2: Norms of Cooperation in Relational Social Capital Enhance MSME Innovation by Facilitating Resource Pooling and Joint Problem-Solving
## iii. Reciprocity within Relational Social Capital
Reciprocity within relational social capital is characterised by a balanced exchange of resources, where network members contribute to and receive support from each other over time (Putnam, 2000). This mutual assistance strengthens the network's resilience and encourages ongoing innovation by establishing a reliable flow of resources and knowledge (Molm, 2003; Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). In MSME networks, reciprocity fosters a supportive environment where firms are motivated to contribute to the collective well-being with the expectation of future support, creating a cycle that reinforces long-term collaboration (Santos, Oliveira, and Curado, 2023; Kim and Shim, 2018). Studies indicate that reciprocal exchanges are crucial for sustaining innovation, as they build trust and reduce the risks associated with collaborative ventures, allowing MSMEs to maintain momentum in their innovation activities (Ganguly, Talukdar, and Chatterjee, 2019; Santos, Oliveira, and Curado, 2023). We hypothesise that reciprocity within relational social capital supports MSME innovation by providing a stable exchange system that enables ongoing resource and knowledge sharing.
H3: Reciprocity within Relational Social Capital Promotes Sustained Innovation by Ensuring a Stable Exchange of Resources
## iv. Identification within Relational Social Capital
Identification refers to the shared sense of belonging and loyalty within a network, where members view themselves as part of a collective and align their actions with common objectives (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998). In networks, identification fosters a unified identity, strengthening trust and collaboration as members work toward shared goals (Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). High levels of identification enhance cohesion within the network, motivating members to contribute knowledge and resources that benefit the group as a whole (Adler & Kwon, 2002; Kankanhalli et al, 2015). This alignment is particularly beneficial for innovation, as it reduces conflicts of interest and encourages members to prioritise collective innovation outcomes over individual gains (Granovetter, 1985). Research suggests that identification within a network enhances resource-sharing behaviours and increases members' commitment to collaborative efforts, which are critical for driving MSME innovation (Moran, 2005). Consequently, we hypothesise that identification within relational social capital positively impacts MSME innovation by fostering a collective commitment to shared goals.
H4: Identification within Relational Social Capital Positively Impacts MSME Innovation by Reinforcing Commitment to Collective Goals
## III. METHODS
### a) Data Collection
To test the study's hypotheses, we conducted a cross-sectional survey targeting owners and managers of textile MSMEs across Nigeria's diverse geopolitical regions. Given their broad oversight of business processes, these individuals are positioned to provide reliable insights into how relational social capital affects innovation within their enterprises. The survey was disseminated online, reaching participants via their trade associations, which helped facilitate broad sector participation and ensured a comprehensive regional spread. A stratified random sampling approach was utilised, allowing for a well-rounded sample of 1,000 textile MSMEs across Nigeria. By sampling from different geopolitical zones, this method aimed to capture cultural nuances that could influence relational social capital, thereby bringing diverse regional perspectives into the study (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998). The focus on textile MSMEs is motivated by the sector's pivotal role in Nigeria's economy, its dependency on social networks for resources and market access, and its unique sectoral challenges, including high competition and resource limitations (Ayyagari, Demirguc-Kunt, & Maksimovic, 2014). Investigating relational social capital in this context provides insight into how elements like trust, cooperation, obligation, reciprocity and identification contribute to fostering the innovation performance of MSMEs across culturally varied environments in Nigeria.
 Fig.1: Conceptual Framework
### b) Sampling
To measure the constructs in our model, we used previously validated scales with minor adjustments to fit the study context (see appendix 2). Each scale included 7 items, and a 5-point Likert scale was employed, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). Translations and cultural adaptations were done for regional relevance, following Sousa and Rojjanasritat's (2011) committee approach to ensure conceptual clarity across For data collection, a questionnaire survey approach was used. To evaluate potential non-response bias, we applied the method outlined by Armstrong and Overton (1977), comparing the responses from the earliest $25\%$ of participants with those from the last $25\%$, using T-tests. Those in the final $25\%$ were respondents who delayed the most in completing the survey after being invited. Since no significant differences were found between these groups, we inferred that non-response bias was unlikely to be a concern. Using G\*Power 3.1, we established a minimum sample size through a power test of 0.8 and an effect size of 0.15 (Faul et al., 2007). With a sample size of 384, the study meets this requirement. Table 4 presents the descriptive statistics.
Table 1: Characteristics of the Sample
<table><tr><td>Item</td><td>Construct</td><td>No</td><td>%</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="2">Gender</td><td>Female</td><td>307</td><td>51.1</td></tr><tr><td>Male</td><td>294</td><td>48.9</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="6">Age</td><td>18-25 years</td><td>206</td><td>34.3</td></tr><tr><td>26 - 35 years</td><td>220</td><td>36.6</td></tr><tr><td>36 - 45 years</td><td>79</td><td>13.1</td></tr><tr><td>46 - 55 years</td><td>68</td><td>11.3</td></tr><tr><td>56 - 65 years</td><td>26</td><td>4.3</td></tr><tr><td>66 > 70 years</td><td>2</td><td>0.3</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="5">Level of Education</td><td>SSCE</td><td>100</td><td>16.8</td></tr><tr><td>Degree</td><td>361</td><td>60.5</td></tr><tr><td>Postgraduate</td><td>80</td><td>13.4</td></tr><tr><td>Others</td><td>15</td><td>2.5</td></tr><tr><td>Diploma</td><td>41</td><td>6.9</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="4">Business Location</td><td>Abia</td><td>116</td><td>19.3</td></tr><tr><td>Oyo</td><td>184</td><td>30.6</td></tr><tr><td>Lagos</td><td>179</td><td>29.8</td></tr><tr><td>Kano</td><td>122</td><td>20.3</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="4">Business Position</td><td>Business Owner</td><td>414</td><td>68.9</td></tr><tr><td>Manager</td><td>56</td><td>9.3</td></tr><tr><td>Staff</td><td>5</td><td>0.8</td></tr><tr><td>Others</td><td>126</td><td>21</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="4">Duration of business owner or manager</td><td>1-5 years</td><td>353</td><td>58.7</td></tr><tr><td>6-10 years</td><td>147</td><td>24.5</td></tr><tr><td>11-20 years</td><td>71</td><td>11.8</td></tr><tr><td>20 years ></td><td>30</td><td>5</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="4">Number of employees</td><td>1-2</td><td>240</td><td>39.9</td></tr><tr><td>3-9</td><td>214</td><td>35.6</td></tr><tr><td>10-49</td><td>125</td><td>20.8</td></tr><tr><td>50-199</td><td>22</td><td>3.7</td></tr></table>
### c) Data Pre-Processing
A normality test was conducted to confirm the model's compatibility with multivariate analysis requirements. Results from the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test indicated that the data did not follow a normal distribution. Thus, PLS-SEM was selected due to its advantages (Hair et al., 2019): (1) suitability for nonnormal data, (2) effectiveness with smaller samples, and (3) applicability for exploratory models. Our study aligns with these conditions, and SmartPLS 4.0 was utilised for the analysis.
### d) Common Method Variance
As this study relies on self-reported data, common method variance (CMV) was evaluated. Initially, Harman's single-factor test identified six distinct factors, with the first factor accounting for $32\%$ of the variance, under the $50\%$ threshold advised by Podsakoff et al. (2003). Additionally, we conducted a supple mentary analysis using the unmeasured latent method construct (ULMC) following Leong et al. (2020). As shown in Appendix B, Table B2, all method loadings were non-significant for each item, while substantive loadings were significant.
## IV. PLS-SEM RESULTS
For empirical analysis, PLS-SEM was employed. According to Hair et al. (2019), this method involves a measurement model for evaluating item reliability and consistency, alongside a structural model for testing convergent and discriminant validity.
### a) Measurement Model Evaluation
The measurement model, or outer model, evaluates both reliability and validity. Regarding item reliability, factor loadings ranged from 0.679 to 0.852 (refer to Table 2). Although Hair et al. (2019) recommends a minimum threshold of 0.708 for reliability, loadings above 0.6 are often sufficient in exploratory studies or when construct validity remains robust (Chin, 1998). Each loading was statistically significant at less than 0.001. Table 5 further shows that Cronbach's alpha values exceeded 0.8, composite reliability (CR) was above 0.8, and rho_A values were over 0.7 (Hair et al., 2019), indicating that the reliability standards were met. Convergent validity was assessed via the average variance extracted (AVE), with values between 0.669 and 0.837, surpassing Hair et al.'s (2019) recommended threshold of 0.5. To verify discriminant validity, the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the Heterotrait-monotrait (HTMT) ratio were applied. The square roots of AVEs on the matrix diagonal were greater than the shared variances among variables, affirming sufficient discriminant validity (Fornell & Larcker, 1981).
According to Hair et al. (2019), model assessment involved examining VIF, $R^2$, $f^2$, the Stone-Geisser ( $Q^2$ ) test, path coefficients, and their significance. The VIF values, ranging from 1.661 to 3.173 (see Table 2), were well below the threshold of 5 (Kock & Lynn, 2012), suggesting no multicollinearity issues. The $R^2$ values reflect the model's explanatory capacity, with the theoretical model accounting for $32.4\%$ of the variance in innovation performance. The $f^2$ effect sizes, representing path coefficient redundancy, ranged from 0.000 to 0.182. Predictive accuracy, assessed via the $Q^2$ value, was found to be 0.305 using blindfolding procedures, indicating moderate predictive power.
## i. Direct Effects Analysis
The results examining relational social capital's impact on MSME innovation performance reveal diverse outcomes across different dimensions. Trust (TRS) exhibited a positive but non-significant effect on innovation performance ( $\beta = 0.094$, $p = 0.177$ ), suggesting that while trust may support innovation, its influence in this study was not statistically substantial. Norms of cooperation (NOC) had a slight negative effect $(\beta = -0.003, p = 0.971)$, indicating minimal impact on MSME innovation. Reciprocity (RECP) also showed a minor negative effect on innovation performance $(\beta = -0.007, p = 0.917)$, implying that expectations of reciprocal support may not significantly foster innovation for MSMEs. However, identification (IDEN) had a pronounced positive impact $(\beta = 0.511, p < 0.001)$, demonstrating that a strong sense of shared identity and alignment within relational social capital significantly enhances innovation performance. These findings suggest that while trust and reciprocity have limited effects, identification plays a critical role in fostering innovation.
Table 2: Reliability and Convergent Validity Analysis for Relational Social Capital Variables
<table><tr><td>Constructs</td><td>Items</td><td>Factor Loading</td><td>rho_c</td><td>Cronbach' α</td><td>rho_A</td><td>AVE</td><td>VIF</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="7">Trust</td><td>TRS1</td><td>0.776</td><td>0.922</td><td>0.902</td><td>0.905</td><td>0.629</td><td>2.028</td></tr><tr><td>TRS2</td><td>0.812</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.288</td></tr><tr><td>TRS3</td><td>0.8</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.281</td></tr><tr><td>TRS4</td><td>0.787</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.163</td></tr><tr><td>TRS5</td><td>0.742</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>1.661</td></tr><tr><td>TRS6</td><td>0.803</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.487</td></tr><tr><td>TRS7</td><td>0.83</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.538</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="7">Norm of Cooperation</td><td>NOC1</td><td>0.747</td><td>0.921</td><td>0.9</td><td>0.908</td><td>0.624</td><td>1.809</td></tr><tr><td>NOC2</td><td>0.816</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.283</td></tr><tr><td>NOC3</td><td>0.796</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.066</td></tr><tr><td>NOC4</td><td>0.816</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.329</td></tr><tr><td>NOC5</td><td>0.827</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.398</td></tr><tr><td>NOC6</td><td>0.744</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.331</td></tr><tr><td>NOC7</td><td>0.78</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.331</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="7">Reciprocity</td><td>REC P1</td><td>0.819</td><td>0.927</td><td>0.909</td><td>0.92</td><td>0.647</td><td>2.322</td></tr><tr><td>REC P2</td><td>0.852</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.786</td></tr><tr><td>REC P3</td><td>0.816</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.32</td></tr><tr><td>REC P4</td><td>0.835</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.507</td></tr><tr><td>REC P5</td><td>0.811</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.357</td></tr><tr><td>REC P6</td><td>0.755</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.325</td></tr><tr><td>REC P7</td><td>0.734</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.249</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="7">Identification</td><td>IDEN1</td><td>0.693</td><td>0.899</td><td>0.869</td><td>0.879</td><td>0.56</td><td>1.686</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN2</td><td>0.8</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.17</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN3</td><td>0.69</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>1.887</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN4</td><td>0.744</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>1.907</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN5</td><td>0.823</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.318</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN6</td><td>0.794</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.08</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN7</td><td>0.679</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>1.834</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="7">Innovation Performance</td><td>IP1</td><td>0.715</td><td>0.953</td><td>0.947</td><td>0.947</td><td>0.593</td><td>2.077</td></tr><tr><td>IP2</td><td>0.747</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.427</td></tr><tr><td>IP3</td><td>0.762</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.309</td></tr><tr><td>IP4</td><td>0.821</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>3.173</td></tr><tr><td>IP5</td><td>0.808</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.813</td></tr><tr><td>IP6</td><td>0.799</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.883</td></tr><tr><td>IP7</td><td>0.791</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.642</td></tr><tr><td>IP8</td><td>0.785</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.641</td></tr><tr><td>IP9</td><td>0.799</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.756</td></tr><tr><td>IP10</td><td>0.764</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.376</td></tr><tr><td>IP11</td><td>0.752</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.445</td></tr><tr><td>IP12</td><td>0.758</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.428</td></tr><tr><td>IP13</td><td>0.764</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.467</td></tr><tr><td>IP14</td><td>0.709</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>2.046</td></tr></table>
The evaluation of the measurement model in this study was conducted using the PLS-SEM approach through the SmartPLS 4.0 software application, focusing on assessing the validity and reliability of the variables involved. This process is crucial for ensuring that the measures used accurately reflect the theoretical concepts they are intended to represent.
Table 3: Fornell-Larcker
<table><tr><td></td><td>IDEN</td><td>IP</td><td>NOC</td><td>RECP</td><td>TRS</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN</td><td>0.748</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>IP</td><td>0.565</td><td>0.77</td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>NOC</td><td>0.702</td><td>0.429</td><td>0.79</td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>RECP</td><td>0.61</td><td>0.367</td><td>0.703</td><td>0.804</td><td></td></tr><tr><td>TRS</td><td>0.637</td><td>0.415</td><td>0.799</td><td>0.649</td><td>0.793</td></tr></table>
Table 4: Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT)
<table><tr><td></td><td>IDEN</td><td>IP</td><td>NOC</td><td>RECP</td><td>TRS</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>IP</td><td>0.606</td><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>NOC</td><td>0.807</td><td>0.45</td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>RECP</td><td>0.695</td><td>0.381</td><td>0.785</td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>TRS</td><td>0.728</td><td>0.438</td><td>0.883</td><td>0.72</td><td></td></tr></table>
In this study, the discriminant validity analysis results are meticulously outlined in Table 2. The table features a correlation matrix in which the diagonal entries represent the square roots of the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) coefficients for each construct. To affirm discriminant validity, the square root of the AVE for any given construct must exceed its highest correlation with any other construct, as posited by Hair et al. (2013). This principle ensures that each construct is sufficiently distinct from the others within the model.
The data presented in Table 4.16 unequivocally demonstrate that for all constructs, the square roots of the AVEs are indeed greater than the corresponding off-diagonal coefficients in both rows and columns of the matrix. This finding firmly establishes the discriminant validity of the constructs, indicating that each construct uniquely captures the phenomenon it is intended to represent, based on their parameter estimates and statistical significance.
Having established the validity and reliability of the constructs through the measurement model, it is imperative to also scrutinise the structural model as a whole. However, prior to delving into the structural model, a critical reassessment of the proposed theoretical framework was conducted. This reassessment was necessitated by modifications made during the confirmatory factor analysis phase, which involved the elimination of certain items. Despite these deletions, it is important to note that no constructs were removed from the model. This decision was based on the criterion that at least two indicators remained to represent each construct adequately, thereby preserving the integrity and coherence of the theoretical framework (Hair et al., 2012). The revised theoretical model of the study is visually depicted in Figure 4.1, showcasing the adjustments made to accommodate the findings from the confirmatory factor analysis and ensure a robust and valid representation of the constructs within the structural model.
Table 5: Overview of Hypothesis Testing Outcomes
<table><tr><td>Hypothesis</td><td>Path coefficient</td><td>Standard deviation</td><td>T statistics</td><td>2.50%</td><td>97.50%</td><td>P values</td><td>Result</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN -> IP</td><td>0.511</td><td>0.060</td><td>8.473</td><td>0.396</td><td>0.630</td><td>0.000</td><td>Accepted</td></tr><tr><td>NOC -> IP</td><td>-0.003</td><td>0.076</td><td>0.037</td><td>-0.154</td><td>0.146</td><td>0.971</td><td>Rejected</td></tr><tr><td>RECP -> IP</td><td>-0.007</td><td>0.066</td><td>0.104</td><td>-0.131</td><td>0.124</td><td>0.917</td><td>Rejected</td></tr><tr><td>TRS -> IP</td><td>0.094</td><td>0.070</td><td>1.352</td><td>-0.044</td><td>0.228</td><td>0.177</td><td>Rejected</td></tr></table>
According to the results, $32.5\%$ of the variance in SMEs innovation performance can be explained by
Trust, Norms of cooperation, Reciprocity and Identification (Figure 7).
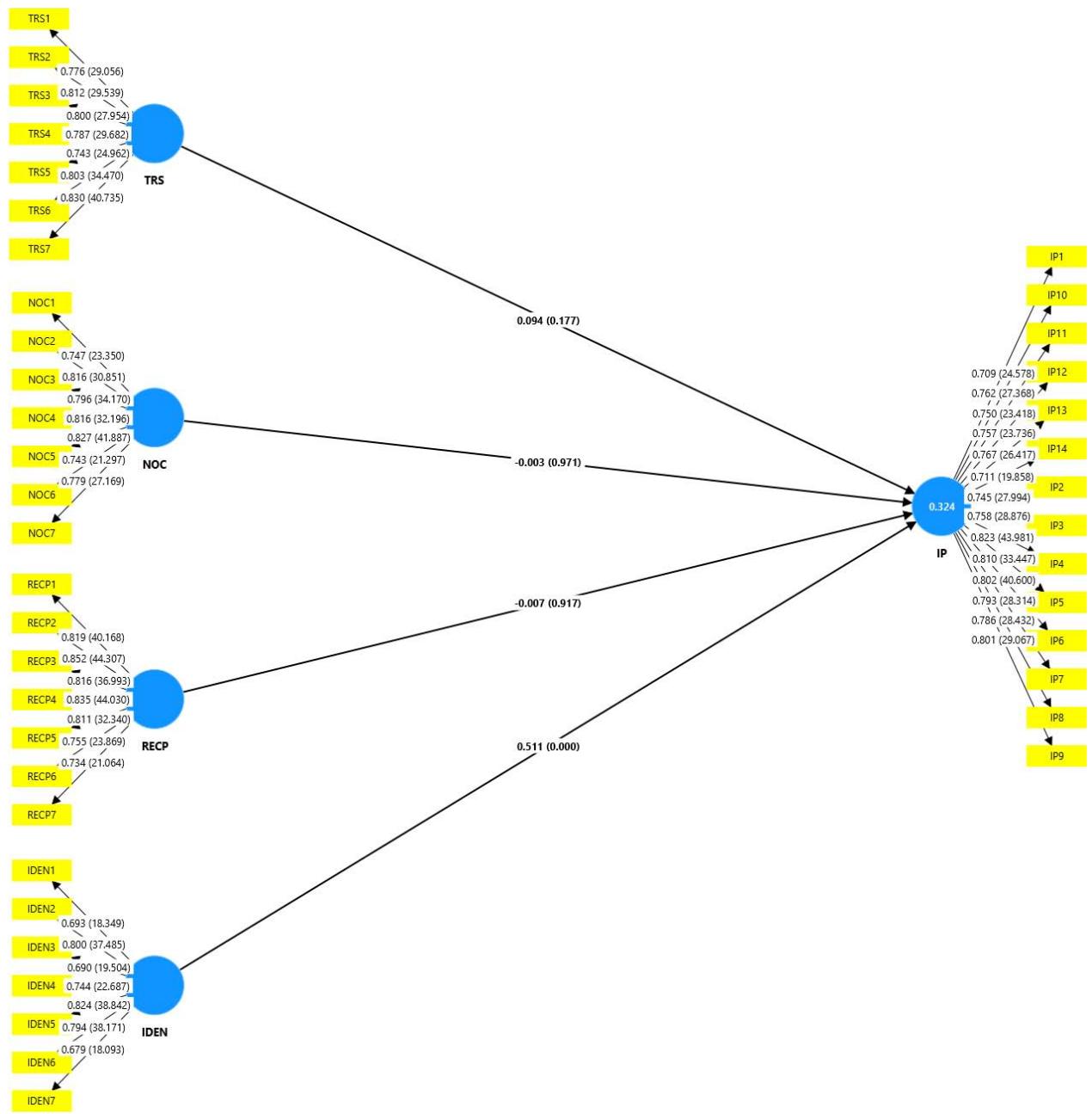 Fig. 2: Path Coefficient Analysis
## V. FSQCA RESULTS
This section details the findings of the fsQCA analysis, focusing on necessary and sufficient conditions for achieving high innovation performance (IP) in MSMEs through components of relational social capital such as trust (TRS), norms of cooperation (NOC), reciprocity (REC), and identification (IDEN). Using a consistency threshold of 0.90 to determine necessity, as suggested by Ragin (2008), we identify configurations that jointly contribute to high IP outcomes. The fsQCA analysis reveals insights into the complex interplay between relational social capital dimensions, highlighting the configurational nature of conditions necessary and sufficient for high innovation.
### a) Calibrating Variables
To convert our causal conditions measured on five-point Likert scales into a fuzzy set scale, we first calculated the average scores for each variable, then determined the percentiles of these averages. Specifically, the full membership threshold was set at the value encompassing $95\%$ of the average scores (fuzzy score $= 0.95$ ). The crossover point was set at the median, covering $50\%$ of the average scores (fuzzy score $= 0.5$ ). The threshold for full non-membership was defined as the value covering the lowest $5\%$ of the average scores (fuzzy score $= 0.05$ ).
### b) Analysis of Necessary Conditions
To identify whether individual relational social capital elements were necessary for achieving high IP, we examined each condition's consistency score, where a score above 0.90 indicates necessity (Ragin, 2008; Schneider & Wagemann, 2010). Table 1 presents the results of the necessary condition analysis.
Table 5: Summary of Analysis of Necessary Conditions
<table><tr><td>Condition</td><td>Consistency</td><td>Coverage</td></tr><tr><td>TRS</td><td>0.861943</td><td>0.976491</td></tr><tr><td>NOC</td><td>0.887297</td><td>0.970939</td></tr><tr><td>REC</td><td>0.869104</td><td>0.973059</td></tr><tr><td>IDEN</td><td>0.923725</td><td>0.971591</td></tr></table>
As shown in Table 5, identification (IDEN) is the only condition with a consistency score exceeding 0.90, indicating it as a necessary condition for high innovation performance. This finding aligns with prior studies suggesting that a strong sense of identification is crucial for effective collaboration and knowledge sharing in MSME networks, which in turn fosters innovation (Fiss, 2011; Schneider et al., 2010). Identification may facilitate trust and commitment within MSMEs, particularly in resource-constrained environments, as it reinforces members' alignment toward common goals (Granovetter, 1985; Adler & Kwon, 2002). The absence of necessity in other conditions suggests that while trust, norms of cooperation, and reciprocity are important, they alone are insufficient to consistently drive high innovation performance without the presence of identification.
### c) Sufficient Configurations of Relational Social Capital
The intermediate solution in fsQCA identifies configurations of relational social capital elements that are sufficient to achieve high IP. These configurations reflect the principle of equifinality, indicating that multiple causal paths can lead to the same outcome, a hallmark of configurational approaches (Ragin, 2008; Fiss, 2011). Table 2 summarises the sufficient configurations derived from the fsQCA analysis.
Table 6: Configurations of fsQCA Intermediate Solution for High Innovation Performance
<table><tr><th>Paths</th><th>TRS</th><th>NOC</th><th>REC</th><th>IDEN</th><th>Raw Coverage</th><th>Consistency</th></tr><tr><td>~TRS * ~NOC * ~REC</td><td>○</td><td>○</td><td>○</td><td>⊗</td><td>0.236973</td><td>0.972811</td></tr><tr><td>TRS * NOC * ~REC</td><td>⊗</td><td>⊗</td><td>○</td><td>⊗</td><td>0.290818</td><td>1.000000</td></tr><tr><td>TRS * NOC * IDEN</td><td>⊗</td><td>⊗</td><td>○</td><td>⊗</td><td>0.828311</td><td>0.987818</td></tr><tr><td>~TRS * ~REC * IDEN</td><td>○</td><td>○</td><td>○</td><td>⊗</td><td>0.260864</td><td>0.997369</td></tr><tr><td>NOC * ~REC * IDEN</td><td>○</td><td>⊗</td><td>○</td><td>⊗</td><td>0.290001</td><td>0.997633</td></tr></table>
The findings reveal five unique configurations that contribute to high IP, underscoring the complex, non-linear relationships among relational social capital elements (Fiss, 2011). For example, in the second configuration (TRS * NOC * ~REC * IDEN), the presence of trust, norms of cooperation, and identification, combined with the absence of reciprocity, consistently leads to high IP with a perfect consistency score of 1.000. This pathway suggests that while reciprocity is generally positive, in some cases, its
absence may streamline interactions and reduce potential conflicts or misunderstandings, facilitating innovation in contexts where consistent cooperation and identification are strongly emphasised (Schneider et al., 2010; Ragin, 2008).
Additionally, the third configuration (TRS * NOC * IDEN) illustrates that when trust, norms of cooperation, and identification are all present, high IP is achieved, highlighting the cumulative impact of these elements on innovation performance. This finding aligns with previous literature that underscores the importance of trust and shared norms in enabling cooperative behaviour and joint problem-solving in MSMEs (Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998; Granovetter, 1985). The overall solution coverage and consistency scores of 0.818 and 0.895, respectively, indicate that these configurations collectively explain a substantial proportion of high innovation performance cases, affirming the robustness of the model. High coverage suggests that the identified configurations encompass a wide range of cases, while high consistency reflects the reliability of these paths in consistently producing the desired outcome (Schneider & Wagemann, 2010; Woodside, 2013). This configurational approach underscores the importance of relational social capital's collective dynamics in driving innovation performance, as opposed to single isolated factors (Fiss, 2011; Ragin, 2008).
In summary, the fsQCA results support the notion that relational social capital influences MSME innovation performance through various combinations of conditions, highlighting the need for tailored strategies that consider specific relational configurations. These findings align with the complementary PLS-SEM results, which identified identification as a significant predictor of innovation performance. Together, both analyses provide a comprehensive understanding of how relational social capital components contribute to MSME innovation within a resource-limited, emerging market context.
## VI. DISCUSSIONS AND CONCLUSION, IMPLICATIONS, AND LIMITATIONS
### a) Discussions and Conclusion
This study explored the impact of relational social capital, specifically trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification on the innovation performance (IP) of MSMEs. By applying both Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA), we aimed to provide a comprehensive view of how these relational dimensions contribute to innovation. The integration of these two methods allows us to validate findings from different perspectives: PLS-SEM identifies significant pathways in a linear context, while fsQCA highlights non-linear, configurational relationships that contribute to high IP in complex, resource-constrained environments like Nigeria.
In the PLS-SEM analysis, identification was found to be a significant predictor of IP in MSMEs, demonstrating that a strong sense of alignment with organisational goals and a shared identity can drive innovation. This result aligns with prior literature suggesting that employees' commitment to collective goals encourages resource sharing and collaborative problem-solving (Levin & Cross, 2004; Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). However, other relational elements trust, norms of cooperation, and reciprocity did not exhibit statistically significant direct effects on IP. This may suggest that, while important, these factors alone do not directly drive innovation but may require specific combinations to be effective.
The fsQCA results complement and extend these findings by identifying five unique configurations that lead to high IP, illustrating the importance of relational elements working in concert. For instance, one configuration showed that the presence of trust, norms of cooperation, and identification, coupled with the absence of reciprocity, is sufficient to achieve high IP. This implies that while reciprocity is generally valuable, its absence in certain configurations may reduce complexity in interactions, fostering a more streamlined approach to innovation (Ragin, 2008; Schneider et al., 2010). Another configuration demonstrated that the combination of trust, norms of cooperation, and identification alone was sufficient to achieve high IP, emphasising that these elements together create a collaborative culture that supports innovation (Granovetter, 1985; Tsai & Ghoshal, 1998). The overall solution coverage and consistency for the fsQCA analysis were 0.818 and 0.895, respectively, indicating that the identified configurations collectively account for a substantial portion of high IP cases. High coverage suggests that these configurations apply to a broad range of cases, while high consistency indicates that these paths reliably lead to the desired outcome (Schneider & Wagemann, 2012; Woodside, 2013). This configurational approach highlights the nuanced ways in which relational social capital elements combine to influence innovation, aligning with previous calls for nonlinear analyses in social capital research (Fiss, 2011; Ragin, 2008).
### b) Theoretical Implications
This study contributes to social capital theory by demonstrating that relational social capital's influence on IP is both context-dependent and configuration-specific. Traditional linear models, such as those applied in PLSSEM, provide a valuable overview but may overlook the complex interdependencies between relational factors. By incorporating fsQCA, our study supports the notion that relational elements must work in specific combinations to foster innovation effectively. This aligns with Fiss's (2011) configurational theory, which posits that specific conditions only lead to desired outcomes when combined in particular ways.
Our findings emphasise the importance of identification as a central driver of innovation within MSMEs, suggesting that alignment with organisational goals and a sense of shared purpose are crucial in resource-limited settings (Coleman, 1988). The role of identification as a core condition in multiple high-IP configurations highlights its significance in relational social capital, adding nuance to existing theories that primarily focus on trust or cooperation as standalone factors (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998; Granovetter, 1985). This study thus contributes to a more refined understanding of relational social capital by illustrating how different configurations can either enable or hinder innovation.
### c) Practical Implications
For managers, these findings suggest that fostering relational social capital requires a balanced approach that considers the specific relational needs of their organisation. Given the central role of identification in our high-IP configurations, managers should cultivate a strong sense of organisational identity and shared goals among employees, as this can significantly enhance innovation outcomes (Levin & Cross, 2004). However, our results also indicate that reciprocity, while valuable, may sometimes complicate relational dynamics, suggesting that managers should carefully assess whether reciprocal relationships are essential or if streamlined interactions are more beneficial in certain contexts.
Additionally, managers should recognize that trust and cooperation are valuable but may need to be coupled with strong identification to drive innovation effectively. Developing initiatives that build trust and cooperation while reinforcing shared goals could foster a collaborative culture that supports innovation. These insights provide actionable guidelines for MSME managers in resource-limited settings, enabling them to strategically leverage relational social capital to improve their innovation capabilities.
### d) Limitations and Future Research
This study has several limitations that provide directions for future research. First, our analysis was limited to the relational dimension of social capital, focusing on a specific subset of MSMEs in Nigeria. Future studies could explore how other social capital dimensions, such as structural and cognitive, interact with relational factors to influence IP. Additionally, while our study utilised both PLS-SEM and fsQCA, future research could apply other non-linear methods or longitudinal designs to capture dynamic relationships over time, particularly as relational networks evolve (Schneider & Wagemann, 2012).
Authorship Contribution Statement
Okechukwu Emmanuel Chiaha: Original draft preparation, methodology, formal analysis, conceptual framework, data curation, investigation, and review and editing of the manuscript.
Adekunle Ogunsade: Supervision, conceptual development, validation, and review and editing of the manuscript.
Oluwasoye Mafimisebi: Supervision, conceptual framework, validation, and manuscript review and editing.
Declaration of Competing Interest
Data Availability: This will be made available on request.
<table><tr><td>Code</td><td>Trust/Trustworthiness: (WeiZheng 2010; Chow and Chan 2008; Hau et al. 2013; Santos et al, 2020)</td></tr><tr><td>TRS1</td><td>I can count on other businesses in my trade when in need.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS2</td><td>I trust other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS3</td><td>I believe other businesses in my trade are honest.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS4</td><td>It's easy for me to rely on other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS5</td><td>I am confident in the businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS6</td><td>Other businesses in my trade usually keep their promises.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS7</td><td>I feel safe doing business with others in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td></td><td>Norms of Cooperation: (Kankanhalli et al, 2015: Santos et al, 2020)</td></tr><tr><td>NOC1</td><td>Businesses in my trade help each other a lot.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC2</td><td>I work well together with other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC3</td><td>I often share tools and ideas with others in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC4</td><td>It's normal for me to team up with other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC5</td><td>I often work with other businesses on big projects.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC6</td><td>In my trade, businesses often come together to solve problems.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC7</td><td>Businesses in my trade usually support each other to do well.</td></tr></table>
<table><tr><td>Code</td><td>Trust/Trustworthiness: (WeiZheng 2010; Chow and Chan 2008; Hau et al. 2013; Santos et al, 2020)</td></tr><tr><td>TRS1</td><td>I can count on other businesses in my trade when in need.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS2</td><td>I trust other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS3</td><td>I believe other businesses in my trade are honest.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS4</td><td>It's easy for me to rely on other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS5</td><td>I am confident in the businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS6</td><td>Other businesses in my trade usually keep their promises.</td></tr><tr><td>TRS7</td><td>I feel safe doing business with others in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td></td><td>Norms of Cooperation: (Kankanhalli et al, 2015: Santos et al, 2020)</td></tr><tr><td>NOC1</td><td>Businesses in my trade help each other a lot.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC2</td><td>I work well together with other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC3</td><td>I often share tools and ideas with others in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC4</td><td>It's normal for me to team up with other businesses in my trade.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC5</td><td>I often work with other businesses on big projects.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC6</td><td>In my trade, businesses often come together to solve problems.</td></tr><tr><td>NOC7</td><td>Businesses in my trade usually support each other to do well.</td></tr></table>
Appendix
<table><tr><td>TRSAV</td><td>NOCAV</td><td>RECAV</td><td>IDENAV</td><td>number</td><td>IPAV</td><td>cases</td><td>raw consist.</td><td>PRI consist.</td><td>SYM consist</td></tr><tr><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>0</td><td>1</td><td>6</td><td>1</td><td></td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>1</td></tr><tr><td>0</td><td>0</td><td>0</td><td>1</td><td>2</td><td>1</td><td></td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>1</td></tr><tr><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>0</td><td>0</td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td></td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>1</td></tr><tr><td>0</td><td>1</td><td>0</td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td></td><td>0.99727</td><td>0.991192</td><td>1</td></tr><tr><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>1</td><td>322</td><td>1</td><td></td><td>0.990734</td><td>0.987707</td><td>0.99771</td></tr><tr><td>0</td><td>0</td><td>0</td><td>0</td><td>4</td><td>1</td><td></td><td>0.969478</td><td>0.871291</td><td>0.883101</td></tr></table>
Generating HTML Viewer...
Funding
No external funding was declared for this work.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
No ethics committee approval was required for this article type.
Data Availability
Not applicable for this article.
Okechukwu Chiaha. 2026. \u201cThe Influence of Relational Social Capital (RSC) on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Innovation Performance: A Mixed Method Study\u201d. Global Journal of Management and Business Research - A: Administration & Management GJMBR A Volume 25 (GJMBR Volume 25 Issue A1): .
This study investigates the influence of relational social capital focusing on trust, norms of cooperation, reciprocity, and identification on innovation performance among Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) within Nigeria’s textile manufacturing sector. Operating in a resource-limited environment, these MSMEs face unique challenges that make relational social capital a critical asset for sustaining competitive advantage and fostering innovation. Using a mixed-method approach, data was obtained from 564 respondents, we integrate Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA) to capture both linear and configurational effects of relational social capital. Results from PLS-SEM reveal that identification significantly enhances innovation performance, while other elements like trust, norms of cooperation and reciprocity exert varied influences. Further, fsQCA identifies five unique configurations of relational social capital elements contributing to high innovation performance, highlighting the essential role of identification alongside specific relational dynamics.
Our website is actively being updated, and changes may occur frequently. Please clear your browser cache if needed. For feedback or error reporting, please email [email protected]
×
This Page is Under Development
We are currently updating this article page for a better experience.
Thank you for connecting with us. We will respond to you shortly.